January 25, 2026 4:32 am
Introduction:
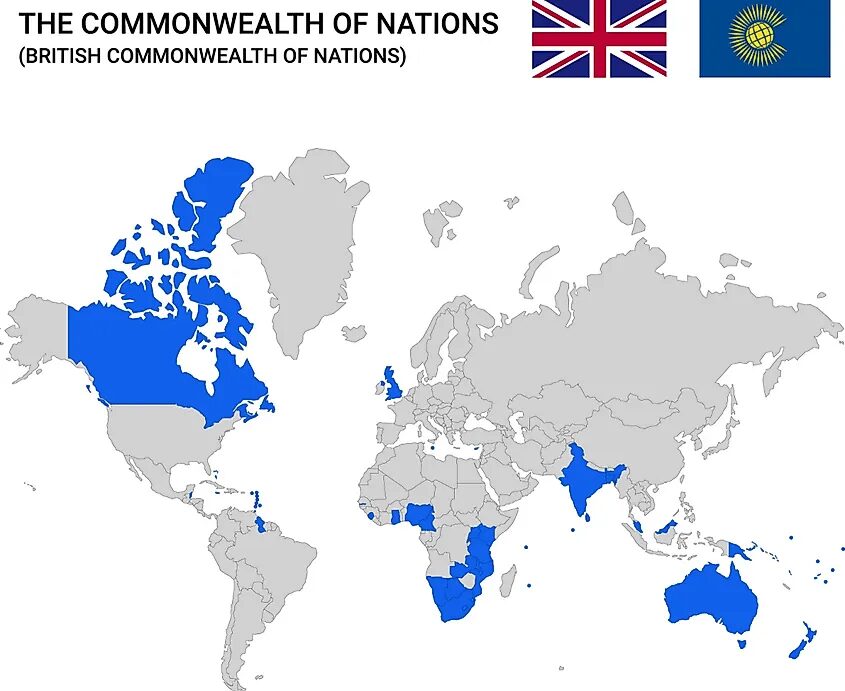
- The Commonwealth of Nations is an intergovernmental organization consisting of 56 member countries, mostly former British colonies.
- It was established by the London Declaration in 1949 to promote sovereignty and self-governance among former colonies of the British Empire.
- Initially created as the British Commonwealth through the Balfour Declaration of 1926 and formalized by the Statute of Westminster in 1931.
- Commonwealth members are united not by legal obligations but by shared values, language, culture, democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, outlined in the Commonwealth Charter.
Structure:
- The Commonwealth fosters economic cooperation and promotes democracy and good governance.
- It is not a political union, meaning the United Kingdom does not wield power over other members.
- The Commonwealth family includes:
- The Commonwealth Secretariat: Supports members in achieving shared goals.
- The Commonwealth Foundation: Encourages public participation in governance.
- The Commonwealth of Learning: Promotes open and distance education.
- Headquarters are located at Marlborough House, London.
- Supported by a network of over 80 intergovernmental, civil, cultural, and professional organizations.
Importance of the Commonwealth:
- Promotes International Cooperation: Facilitates dialogue on economic development, trade, and environmental sustainability.
- Strengthens Democratic Values: Supports democracy and good governance.
- Encourages Cultural Exchange: Initiatives like the Commonwealth Cultural Fund and Commonwealth Writers’ Prize promote cultural understanding.
- Provides Assistance: Offers technical expertise and financial aid for development goals.
- Advocates for Small States: Ensures small states’ interests are represented in global discussions.
India and the Commonwealth:
- India joined the Commonwealth in 1947 after gaining independence from British rule.
- Key historical events include:
- 1947: India becomes a member upon independence.
- 1950: India remains in the Commonwealth after becoming a republic.
- 1983: Hosted the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM) in New Delhi.
- 2013: Hosted CHOGM in Colombo, Sri Lanka.
- 2018: Became the Chair-in-Office of the Commonwealth.
- India has significantly contributed to economic development and cooperation within the Commonwealth.
Significance for India:
- Economic Cooperation: Engages with member states on trade and economic issues.
- Cultural Exchange: Strengthens ties through cultural initiatives.
- Development Assistance: Benefits from financial and technical support.
- Democratic Values: Reinforces democratic principles and governance.
- Support for Small States: Advocates for inclusion in global decision-making.
- Strategic Importance: Provides a platform to counter rivals, especially given China’s non-membership.
Issues:
- Declining Relevance: The organization’s influence is waning.
- Limited Power: As a voluntary association, it struggles to enforce decisions.
- Funding Constraints: Relies on member and donor contributions, limiting resources.
- Lack of Clear Mandate: Without a formal charter, diverse priorities hinder consensus and effectiveness.
Way Forward:
- Establish a Clear Mandate: Developing a formal charter could provide clearer objectives.
- Expand Membership: Including more countries that align with Commonwealth values could boost influence.
- Increase Transparency: Building trust through transparent decision-making processes.
- Focus on Key Issues: Deepen cooperation on trade, economic growth, and sustainability through joint initiatives.
Conclusion:
- India’s renewed interest in the Commonwealth is promising, aiming to shape a forward-looking agenda.
- By leveraging its membership, India can enhance trade, build consensus on global reforms, and strengthen bilateral relations.
- The Commonwealth offers a multilateral platform for India to advance global economic stability and promote collaborative solutions to international challenges.
Current Affairs for Commonwealth Nations
Diplomatic Relations: India-Canada Tensions
- India has strongly criticized Canada’s recent allegations linking India’s Home Minister, Amit Shah, to supposed plots against Sikh separatists in Canada. India has termed these accusations as “absurd and baseless.”
- The Indian government has warned that such unfounded claims could severely damage the diplomatic relationship between the two nations, adding tension to an already strained situation.
2. Defense and Security: Inauguration of India’s First Private Military Aircraft Facility
- India has opened its first private military aircraft manufacturing facility in Gujarat, a significant milestone in boosting domestic defense manufacturing.
- The facility is a joint venture between Tata and Airbus and will produce C-295 military aircraft for the Indian Air Force. This initiative will strengthen India’s defense capabilities and promote self-reliance in defense manufacturing, while also creating job opportunities.
3. Economy: India’s Economic Growth Forecast
- The Indian government has released a report maintaining an economic growth forecast of 6.5% to 7% for the current fiscal year. Despite external challenges like global geopolitical conflicts and trade uncertainties, the report remains optimistic.
- Positive factors include a strong agricultural output and increased consumer demand during the festive season. However, the government acknowledges risks from international events that could impact economic stability.
4. International Relations: SCO Membership Expansion
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) has expanded by admitting Iran as a full member, enhancing its geopolitical and strategic influence across Eurasia.
- This move underscores the growing significance of the SCO in regional politics, economics, and security cooperation, and strengthens ties among member nations, which include India, China, and Russia.
5. Technology and Innovation: AI Collaboration between IndiaAI and Meta
- IndiaAI and Meta (formerly Facebook) have partnered to establish the Center for Generative AI, named ‘Srijan,’ at IIT Jodhpur. This center aims to advance research and development in open-source artificial intelligence within India.
- Additionally, the YuvAi Initiative will focus on training and building skills related to AI, supporting India’s growing technological ecosystem and encouraging innovation.
6. Environment: Climate and Health Africa Conference (CHAC 2024)
- The first-ever Climate and Health Africa Conference (CHAC 2024) is being held in Harare, Zimbabwe. This conference aims to integrate African nations into the global dialogue on climate change and health, addressing the unique challenges faced by the continent.
- Representatives from 54 African countries are attending, highlighting the need for coordinated action to address climate change’s impact on health.





[…] THE COMMONWEALTH OF NATIONS […]
[…] THE COMMONWEALTH OF NATIONS […]