For Prelims: Jharkhand Economy, jharkhand economy pdf, jharkhand economy notes pdf
For Mains: Jharkhand Economy, jharkhand economy pdf, jharkhand economy notes pdf
*
Introduction to Jharkhand Economy
The Jharkhand economy has witnessed gradual progress, with significant contributions from mineral resources, industries, agriculture, and emerging services sectors. While the industrial and mining sectors have driven economic growth, the agriculture and tourism sectors remain underutilized, reflecting challenges and opportunities for sustainable development.
[](https://learnpro.graphy.com/courses/14th-JPSC-Prelims-Course-2025-675eeda63e7d000741bcc01f)
Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of Jharkhand
The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of Jharkhand has shown significant recovery post-pandemic. Despite economic challenges, the Jharkhand economy is projected to continue growing at a steady pace.
Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) is the total value of all goods and services produced within a state's borders over a specific period of time. It's a key indicator of a state's economic growth and is the counterpart to the national gross domestic product (GDP).
#### GSDP Growth Trends:
1. Post-COVID Recovery:
- The GSDP contracted during 2020-21 due to the nationwide lockdown and pandemic-induced slowdown. It stood at ₹2,19,483 crore at constant prices and ₹2,96,664 crore at current prices during this year.
- Since 2021-22, Jharkhand’s economy has exhibited consistent recovery.
2. Recent Growth Performance:
- Between 2020-21 and 2022-23, the GSDP grew at an average annual rate of 8.8% at constant prices.
- The growth rate of the nominal GSDP (current prices) averaged 15.2% during the same period, showcasing strong resilience.
3. GSDP Projections:
- For the financial year 2023-24, the GSDP is estimated to grow by 7.1% at constant prices and 8.7% at current prices.
- Projected GSDP:
- Constant Prices: ₹2,78,316 crore.
- Current Prices: ₹4,28,155 crore.
- For 2024-25, the state’s GSDP is forecasted to increase by 7.7% at constant prices and 9.8% at current prices.
- Projected GSDP:
- Constant Prices: ₹2,99,843 crore.
- Current Prices: ₹4,70,104 crore.

GSDP at Constant Prices (Rs. Crores) and the Growth Rate (in percentage)
#### GSDP Contribution to India’s Economy:
- Jharkhand’s GSDP accounts for approximately 1.62% of India’s overall GDP.
- Although the state contributes disproportionately less compared to its share of the national population (2.7%) and geographical area (2.4%), its economic share has gradually improved post-2019.
#### Per Capita Income Trends: (Jharkhand Economy)
- 2020-21:
- At current prices: ₹69,963.
- 2022-23:
- At current prices: ₹91,874.
- 2023-24 Estimates:
- At current prices: ₹98,649.
- 2024-25 Forecast:
- At current prices: ₹1,07,027.

Per Capita Income Trends: (Jharkhand Economy)
#### Comparison with National Growth:
- Between 2020-21 and 2022-23, Jharkhand’s GSDP grew at a faster pace (8.8%) than the national GDP (8.1%).
- This trend underscores the resilience of Jharkhand Economy in the face of economic disruptions and its ability to outpace national growth rates.
*
#### Key Takeaways:
- The steady increase in GSDP, coupled with strong recovery trends, indicates positive economic momentum in Jharkhand Economy.
- Focus on infrastructure development, industrial growth, and economic diversification will be crucial for sustaining this growth trajectory of Jharkhand Economy.
- Improvements in per capita income demonstrate better income distribution, though gaps remain in underperforming sectors like agriculture of Jharkhand Economy.
*
Sector-Wise Analysis of Jharkhand Economy
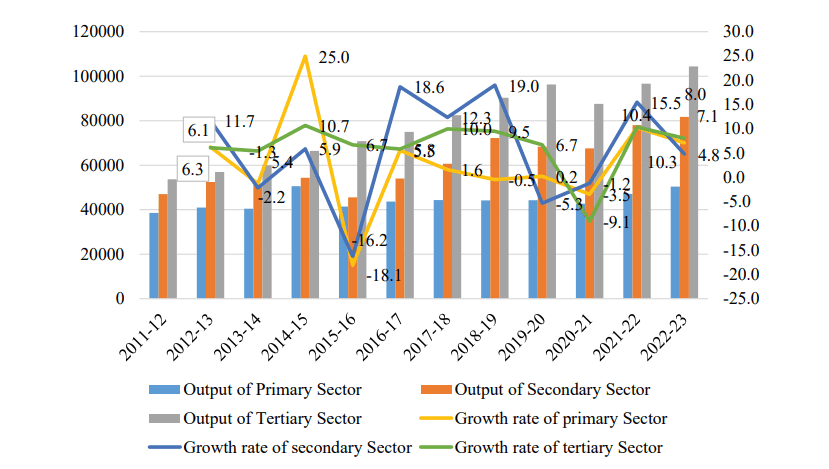
The GSVA of the Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sectors (in Rs. crores) and their
Growth-Rate (in %) in Jharkhand Economy
A. Primary Sector (Agriculture, Forestry, Animal Husbandry, and Fishing):
The primary sector remains critical for Jharkhand economy, though its share in the Gross Value Added (GVA) has shown modest growth. Agriculture, forestry, and fishing play a central role in rural livelihoods.
Gross value added (GVA) is the measure of the total value of goods and services produced in an economy( area, region or country). The amount of value-added to a product is taken into account
1. Contribution to GVA:
- In 2022-23, the primary sector contributed 21.3% to Jharkhand’s GVA, showing a consistent decline compared to past decades.
- The sector’s CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) between 2011-12 and 2022-23 remained low at 3.1%, reflecting stagnant productivity and variability.
2. Agricultural Production Trends:
- Key Crops: Paddy remains the primary crop in Jharkhand Economy, followed by maize, pulses, and oilseeds.
- Paddy:
- Production peaked at 5.36 million tonnes in 2021-22 but fell to 1.82 million tonnes in 2022-23 due to erratic rainfall.
- For 2023-24, paddy production is expected to recover to 2.57 million tonnes.
- Maize: Production declined from 623.4 thousand tonnes in 2021-22 to 402.1 thousand tonnes in 2022-23, with a projected recovery to 504.5 thousand tonnes in 2023-24.
3. Horticulture and Allied Sectors:
- Vegetables: Output grew marginally from 293.88 thousand tonnes (2018-19) to 305.28 thousand tonnes (2022-23).
- Fruits: Area under fruit cultivation expanded to 111.36 thousand hectares, though production slightly declined to 1.26 million tonnes.
4. Animal Husbandry and Fisheries:
- Milk Production: Increased significantly from 1.89 million tonnes in 2017-18 to 2.57 million tonnes in 2021-22.
- Meat Production: Grew from 0.55 lakh tonnes to 0.79 lakh tonnes over the same period.
- Fish Production: Reached 2.57 lakh tonnes in 2021-22, highlighting steady growth in the fisheries sector.
5. Irrigation Coverage:
- The gross irrigated area increased to 2.91 lakh hectares in 2021-22 but remains inadequate, covering only a fraction of Jharkhand's total cultivable land.
- Key Sources: Wells dominate irrigation, followed by tanks, canals, and sustainable practices like sprinkler and drip irrigation.
6. Challenges in Agriculture in Jharkhand Economy:
- Irrigation Deficit: Limited coverage remains a significant barrier.
- Fragmented Land Holdings: Over 70% of agricultural holdings are marginal, averaging less than 1 hectare.
- Climate Variability: Fluctuating monsoons and climate change adversely impact crop yields.

Share of the Sub sectors of Primary Sector in the GVA
Government Schemes for Agriculture and Allied Activities in Jharkhand Economy
The Government of Jharkhand has implemented several targeted schemes to address challenges in agriculture, irrigation, allied sectors, and farmers' welfare. These schemes aim to improve productivity, promote modern practices, and enhance income levels for small and marginal farmers and boost Jharkhand Economy .
[](https://learnpro.graphy.com/courses/14th-JPSC-Test-Series--6752fcb6da6f046a25e90f7e)
*
#### 1\. Jharkhand Kisan Fasal Rahat Yojana (Jharkhand Economy)
- Objective: Provides a security cover for farmers against crop damage caused by natural calamities.
- Key Features:
- Ensures timely financial support to help farmers recover from losses.
*
#### 2\. Mukhyamantri Krishi Ashirwad Yojana (MKAY)
- Objective: Financial assistance for small and marginal farmers.
- Details:
- Benefits are directly transferred to farmers’ bank accounts via DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer).
*
#### 3\. Samekit Birsa Gram Vikas Yojana cum Krishak Pathshala (Jharkhand Economy)
- Objective: Promotes the adoption of modern agricultural technologies and capacity building.
- Features:
- Provides practical training to farmers to enhance productivity and income.
*
#### 4\. Birsa Kisan Yojana (BKY)
- Objective: Ensures streamlined access to government schemes for farmers.
- Details:
- Enables quick identification and access to benefits under various agricultural schemes.
*
#### 5\. Jharkhand e-Uparjan Portal (Jharkhand Economy)
- Objective: Digitizes the agricultural procurement process to ensure transparency and efficiency.
- Key Features:
- Ensures Minimum Support Price (MSP) payments directly into farmers’ bank accounts.
- Reduces middlemen interference and promotes timely payments.
*
#### 6\. Soil and Water Conservation Scheme (Jharkhand Economy)
- Objective: Reduces soil erosion and promotes sustainable water conservation.
- Budget and Targets for FY 2023-24:
- Targets include construction of 3,310 percolation tanks and 1,170 deep borings.
*
#### 7\. Jalnidhi Yojana (Jharkhand Economy)
- Objective: Ensures groundwater recharge and availability for irrigation.
- Details:
- Significant for improving irrigation coverage in rain-fed areas.
*
#### 8\. Agri Export and Agri Marketing cum Post-Harvest Infrastructure Development Scheme (Jharkhand Economy)
- Objective: Enhances post-harvest infrastructure and boosts agricultural exports.
- Details:
- Budget allocation: ₹1,000 lakh for FY 2023-24.
*
#### 9\. National Mission on Agricultural Extension and Technology
- Objective: Provides farmer-driven technology dissemination and capacity-building initiatives.
- Budget Allocation for FY 2023-24: ₹2,188.31 lakh.
- Activities: Includes training, demonstrations, and farmer-scientist interactions.
*
#### 10\. Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
- Objective: Promotes integrated and state-specific agricultural development.
- Features:
- Focuses on achieving 4% annual agricultural growth through state-level initiatives.
*
#### 11\. Integrated Birsa Village Development Scheme
- Objective: Develops villages into agricultural hubs with farmer clusters.
- Progress:
- Targets the establishment of Krishak Pathshalas to provide structured training and demonstration of modern farming practices.
*
#### 12\. Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY)
- Objective: Expands irrigation coverage and improves water use efficiency.
- Achievements:
- Ensures sustainable water management practices
*
B. Secondary Sector (Industries, Mining, and Construction) in Jharkhand Economy
The Secondary Sector forms the backbone of Jharkhand economy due to its vast mineral resources, robust industrial infrastructure, and expanding construction activities. It contributes significantly to the state's Gross Value Added (GVA) and employment generation, making it a key driver of economic growth.
*
#### 1\. Contribution to GVA and Growth Trends
- In 2022-23, the Secondary Sector accounted for 33.5% of Jharkhand's GVA.
- The sector experienced a growth rate of 4.8% during 2022-23, showcasing resilience despite global challenges like commodity price fluctuations and market volatility.
*
#### 2\. Industries and Manufacturing
The industrial sector in Jharkhand is heavily dependent on mining and quarrying due to the state's abundant natural resources. The state is home to numerous heavy industries, steel plants, and manufacturing units.
##### Mining and Quarrying
- Jharkhand's Share in India’s Mineral Wealth:
- The state is rich in coal, iron ore, copper, mica, bauxite, and limestone, which form the base for various heavy industries.
- Coal Production:
- In 2022-23, coal production reached 157.96 lakh tonnes, enabling industrial growth and power generation across India.
- Major coalfields include:
- Jharia Coalfield (largest coal reserve in India).
- Bokaro Coalfield.
- North Karanpura Coalfield.
- Iron Ore and Other Minerals:
- Copper mining takes place in Singhbhum district, supporting industrial processes.
- Mica, bauxite, and limestone further support allied industries like cement, aluminum, and electrical equipment production.
#### Industrial Growth and Manufacturing in Jharkhand Economy
Jharkhand’s industrial base is supported by major manufacturing hubs in Jamshedpur, Bokaro, and Dhanbad.
- Key Industries:
- Tata Motors (TELCO): Manufactures heavy commercial vehicles, contributing to the automotive sector.
- Usha Martin: Known for producing high-quality wire ropes with global exports.
- Hindalco Industries: Processes bauxite into aluminum products.
- Growth Trends in Manufacturing:
- The Jharkhand Industrial Promotion Policy has been a key initiative to attract investments, modernize industries, and promote Ease of Doing Business in the state.
*
#### 3\. Construction and Infrastructure (Jharkhand Economy)
The Construction Sector has emerged as a critical growth area within the secondary sector, driven by increasing public and private investments.
- Growth Rate: The sector grew by 7.9% in 2022-23, demonstrating significant progress in infrastructure projects.
#### Infrastructure Development Initiatives (Jharkhand Economy)
1. Road and Transport Connectivity:
- Expansion of national highways, state highways, and rural roads under schemes like Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY).
- Notable projects include upgrading connectivity to major industrial hubs like Bokaro, Jamshedpur, and Ranchi.
2. Urban Infrastructure:
- Focus on improving urban amenities and promoting smart city projects in Ranchi under the Smart Cities Mission.
- Development of sewage systems, urban housing, and smart public infrastructure.
3. Power and Energy Projects:
- Investment in renewable energy projects, including solar and hydroelectric power plants, to meet rising energy demands.
- Upgrading thermal power plants for efficiency.
4. Industrial Infrastructure:
- The government is investing in industrial corridors and Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to attract global investments.
- Prominent industrial parks include Adityapur Industrial Area and Bokaro Industrial Park.
#### Impact of Infrastructure Growth in Jharkhand Economy
- Enhances employment opportunities in construction-related activities.
- Improves connectivity, supporting transportation of minerals and manufactured goods.
- Promotes ease of doing business, attracting domestic and foreign investments.
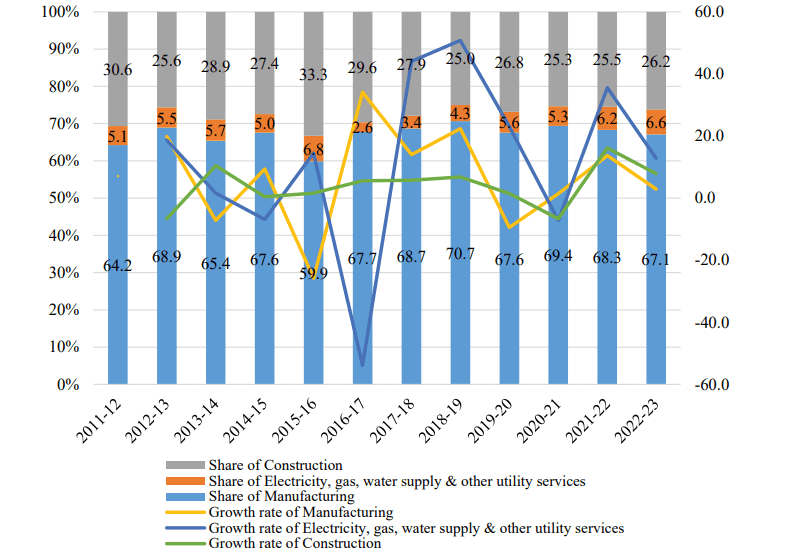
Constituents of the Secondary sector in its GVA
*
#### Government Policies for the Secondary Sector of Jharkhand Economy
The Jharkhand Industrial Promotion Policy and other initiatives aim to modernize industries, attract investments, and foster sustainable growth:
1. Jharkhand Industrial Promotion Policy (JIPP):
- Offers incentives like subsidized land, power rebates, and tax exemptions for new industries.
- Focuses on promoting sectors such as steel, cement, automotive, textiles, and IT industries.
2. Jharkhand Electric Vehicle Policy:
- Encourages manufacturing of electric vehicles, batteries, and associated infrastructure to reduce environmental impact and boost new-age industries.
3. District Mineral Foundation (DMF) Funds:
- Revenue collected from mining is reinvested in infrastructure, healthcare, education, and welfare schemes for mining-affected communities.
4. Ease of Doing Business Initiatives:
- Single-window clearance for industries to streamline approvals and investments.
*
#### Significance of the Secondary Sector
The Secondary Sector remains Jharkhand’s economic driver for the following reasons:
- Revenue Generation: Jharkhand earns significant revenue through mining royalties and industrial output.
- Employment Creation: Mining, construction, and manufacturing provide employment to millions, particularly in urban and semi-urban regions.
- Economic Diversification: Promotes industrial and infrastructure growth, reducing dependence on the primary sector.
*
#### Challenges in the Secondary Sector
- Environmental Impact: Extensive mining leads to deforestation, soil degradation, and water pollution.
- Resource Exhaustion: Overreliance on mineral wealth risks resource depletion.
- Industrial Diversification: Limited diversification beyond mining and steel industries hampers balanced growth.
- Skill Gap: Lack of skilled labor to meet the demands of modern industries.
*
C. Tertiary Sector (Services and Trade) in Jharkhand
The Tertiary Sector has emerged as the fastest-growing segment of Jharkhand's economy, reflecting structural transformation toward a service-oriented economy. The sector's increasing share in the state's Gross Value Added (GVA) highlights its pivotal role in driving economic growth and employment.
*
#### 1\. Contribution to GVA
- In 2022-23, the tertiary sector contributed 43.2% to Jharkhand's total GVA, maintaining its dominant position.
- Over the last decade (2011-12 to 2022-23), the sector grew at an average annual rate of 6.2%, surpassing the growth of the primary and secondary sectors.
#### Growth Trends
- The sector's output contracted sharply by 9.1% in 2020-21 due to the COVID-19 pandemic but rebounded by 10.4% in 2021-22 and grew further by 8% in 2022-23, signaling a strong recovery.
*
#### 2\. Key Sub-Sectors in the Tertiary Sector
##### i. Trade, Repair, Hotels, and Restaurants
- This sub-sector is the fastest-growing component, expanding at an average annual growth rate of 8.5% between 2011-12 and 2022-23.
- In 2022-23, its share in the GVA of the tertiary sector reached 27%, up from 21.5% in 2011-12.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic caused a contraction of 17.3% in 2020-21. However, it rebounded with growth rates of 10.4% in 2021-22 and 5.5% in 2022-23.
*
##### ii. Transport, Storage, and Communication
- This sub-sector experienced an average growth rate of 5.5% between 2011-12 and 2022-23.
- Post-pandemic recovery: The sub-sector grew by 23.2% in 2021-22 and 6.7% in 2022-23.
- Air Transport: Despite contributing a small share, it has been the fastest-growing component within this sub-sector, with an average growth rate of 20.6% from 2011-12 to 2022-23.
- Storage Sector: Grew marginally at 0.6% CAGR, reflecting its underdeveloped potential.
*
#### iii. Financial and Real Estate Services
- Financial Services: Contributed 6.8% to the GVA of the tertiary sector in 2022-23, declining from 7.7% in 2011-12 due to slower growth at an annual average rate of 5.1%.
- Real Estate and Professional Services: The share of this sub-sector remained steady at around 21.9% in 2022-23, growing at a rate of 6.9% annually.
*
#### iv. Public Administration and Other Services
- Public Administration: Its share declined from 18.3% in 2011-12 to 12.4% in 2022-23, with a slow annual growth rate of 2.6%.
- Other Services: Improved its share from 13.7% in 2011-12 to 15% in 2022-23, growing at an annual rate of 7.1%, reflecting the increasing demand for social and personal services.
*
#### 3\. Tourism and Emerging Sectors
##### Tourism Sector
- Jharkhand possesses immense potential for eco-tourism, religious tourism, and cultural heritage. Major attractions include:
- Natural Sites: Betla National Park, Netarhat, and Hundru Falls.
- However, the sector remains underdeveloped due to inadequate infrastructure, promotion, and investment.
*
#### Cottage Industries and IT Sector
- Cottage Industries: Jharkhand promotes small-scale industries such as handloom, sericulture, and handicrafts. Organizations like JHARCRAFT support artisans with training, raw materials, and market access.
- Information Technology (IT): Government incentives under the Jharkhand Industrial and Investment Promotion Policy aim to attract IT investments and establish technology hubs to create employment and diversify the economy.
- Emerging IT parks and cottage industries such as silk production add to state revenue.
- JASCOLAMF: Promotes lac production and export. VEGFED: Supports vegetable farmers by organizing marketing activities. JHAMCOFED: Develops and markets minor forest produce to enhance tribal incomes.
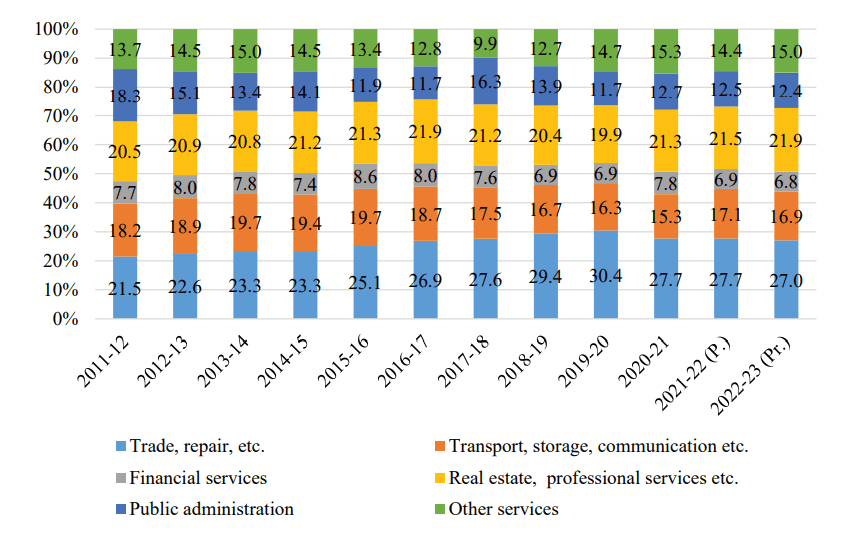
Share of the Sub -Sectors in the Output of the Tertiary Sector
*
#### 4\. Challenges in the Tertiary Sector
- Infrastructure Gaps: Limited transport and communication networks hinder trade and logistics.
- Tourism Underdevelopment: Inadequate promotion and infrastructure limit Jharkhand's tourism potential.
- Service Quality: Slow growth in financial and public administration services indicates inefficiencies and low innovation levels.
*
#### 5\. Government Initiatives
- Jharkhand Industrial Promotion Policy: Supports IT, tourism, and service sector investments through incentives and infrastructure development.
- Smart Cities Mission: Development of Ranchi as a smart city to boost urban services.
- Skill Development Programs: Capacity-building initiatives to improve the quality of service sector employment.
Key Challenges in Jharkhand Economy
- Agricultural Stagnation: Low irrigation, fragmented land holdings, and outdated technology.
- Overdependence on Mining: Environmental degradation and resource depletion due to overreliance on mineral extraction.
- Limited Industrial Diversification: Industries are concentrated in specific regions, leading to unequal growth.
- Underdeveloped Tourism: Poor infrastructure restricts the sector’s potential.
- Social Inequality: Marginalized communities (SC/ST/OBC) remain underrepresented in economic benefits.
*
Government Strategies for Economic Development
- Agriculture: Expansion of irrigation, crop diversification, and promotion of cooperatives.
- Industries: Infrastructure investment and industrial incentives to attract businesses.
- Social Sector: Allocations for education, healthcare, and welfare of marginalized communities.
*
Conclusion
The Jharkhand economy has immense potential for growth driven by its mineral wealth, industrial capacity, and agricultural reforms. Government initiatives focusing on infrastructure, irrigation expansion, industrial diversification, and tourism development are critical to ensuring inclusive and sustainable growth. By addressing key challenges and harnessing untapped opportunities, Jharkhand can achieve a robust economic transformation.
Further Reading
- Learn more about India’s GSDP trends: [Economic Survey of India](https://www.indiabudget.gov.in)
- Explore Jharkhand’s Industrial Policy: [Government of Jharkhand](https://www.jharkhand.gov.in)
- Skill Development Programs: [PMKVY Official Site](https://pmkvyofficial.org)
- JPSC official Site : [https://www.jpsc.gov.in/](https://www.jpsc.gov.in/)
##### Posts related to JPSC on LearnPro’s website:
- [JPSC Notes](https://learnpro.in/jpsc-notes/?utm_source=chatgpt.com): Access expertly curated notes covering essential topics for both JPSC Prelims and Mains exams.
- [14th JPSC PT Exam Comprehensive Test Series](https://learnpro.in/14th-jpsc-pt-exam-with-comprehensive-test-series/?utm_source=chatgpt.com): Enhance your preparation with a structured test series designed to cover all aspects of the JPSC Preliminary Test syllabus, emphasizing Jharkhand-specific topics and current affairs.
- [JPSC Notification 2024](https://learnpro.in/jpsc-notification-2024-out-check-jharkhand-psc-mains-exam-date/?utm_source=chatgpt.com): Stay informed about the latest updates, including exam dates, eligibility criteria, and vacancy details for the JPSC 2024 examination.
- [General Introduction to Jharkhand for JPSC Exam](https://learnpro.in/general-introduction-to-jharkhand-for-jpsc-exam/?utm_source=chatgpt.com): Gain a comprehensive understanding of Jharkhand’s history, geography, economy, and culture, crucial for the JPSC exam.