India’s Infrastructure Development
Infrastructure is the backbone of a country’s economic growth, social development, and global competitiveness. For India, a rapidly growing economy with aspirations to become a $5 trillion economy, robust infrastructure is critical. From roads and railways to energy and digital connectivity, infrastructure impacts every aspect of the economy. However, the sector faces significant challenges, including funding gaps, project delays, and regional disparities.
Importance of Infrastructure Development
Economic Impact
- Infrastructure contributes to GDP growth by enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and creating jobs.
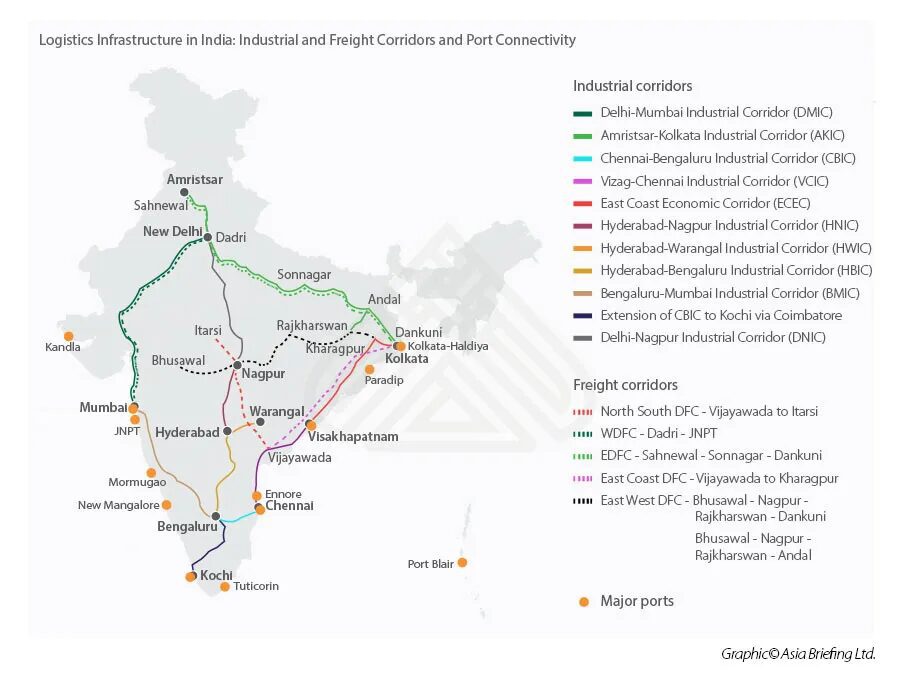
- Improved logistics through highways, railways, and ports reduce supply chain inefficiencies.
Social Development
- Access to quality infrastructure like healthcare facilities, schools, and drinking water improves the quality of life.
- Connectivity in rural areas reduces regional inequalities and urban-rural divides.
Global Competitiveness
- Quality infrastructure enhances India's attractiveness as an investment destination.
- Improved global rankings in indices like the Ease of Doing Business and Global Competitiveness Index reflect robust infrastructure.
Key Sectors of Infrastructure in India
Roadways
- India has the second-largest road network in the world, spanning 6.2 million km.
- National Highways Development Project (NHDP) has been instrumental in expanding highways.
Railways
- Indian Railways is the fourth-largest railway network globally, transporting over 8 billion passengers annually.
- Initiatives like high-speed rail projects aim to modernize the network.
Energy
- India is the third-largest producer and consumer of electricity.
- Renewable energy contributes over 26% of the total installed capacity.
Ports
- Major ports handle over 60% of India’s trade by volume.
- Development of Sagarmala Project aims to enhance port-led industrialization.
Urban Infrastructure
- With over 31% of the population living in urban areas, the focus is on smart cities, housing, and urban mobility.
Digital Infrastructure
- India is the second-largest internet market globally, with over 700 million users.
- Digital India Programme aims to bridge the digital divide.
Challenges in India’s Infrastructure Development
Funding Gaps
- The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) projects a need for ₹111 lakh crore investment by 2025.
- Public-private partnerships (PPPs) face delays due to regulatory issues and lack of investor confidence.
Land Acquisition Issues
- Acquiring land for infrastructure projects often leads to delays and cost escalations.
- Resistance from local communities and lengthy approval processes exacerbate the problem.
Project Delays
- Over 450 infrastructure projects are delayed due to factors like red tape, resource shortages, and weak project management.
Regional Disparities
- States like Bihar and Odisha lag behind in infrastructure development compared to Maharashtra or Gujarat.
Environmental Concerns
- Large-scale projects often face opposition due to ecological damage, deforestation, and displacement.
Governance and Regulatory Hurdles
- Coordination challenges among multiple ministries and agencies hinder effective implementation.
- Corruption and inefficiency add to the burden of infrastructure costs.
Government Initiatives for Infrastructure Development
National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
- Aimed at improving infrastructure across energy, transport, water, and social sectors.
- Focuses on enhancing private sector participation and reducing funding gaps.
Bharatmala Pariyojana
- Aims to develop 34,800 km of highways, focusing on economic corridors and border connectivity.
Sagarmala Project
- Enhances port-led development through modernization of ports and connectivity improvements.
- Promotes coastal economic zones and inland waterways.
Smart Cities Mission
- Focuses on developing 100 smart cities with sustainable and technology-driven solutions.
Digital India Programme
- Bridges the digital divide by enhancing broadband connectivity, e-governance, and digital literacy.
PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan
- A multimodal connectivity plan to integrate railways, roads, ports, and airports.
- Aims to reduce logistics costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
Recent Progress and Achievements
Transport Infrastructure
- Roads: Expansion of expressways like the Delhi-Mumbai Expressway ensures faster connectivity.
- Railways: Introduction of semi-high-speed trains like Vande Bharat improves passenger experience.
- Airports: Development of greenfield airports under the UDAN Scheme boosts regional air connectivity.
Energy Sector
- Renewable Energy Targets: India aims to achieve 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
- Grid Modernization: Smart grids and transmission lines enhance energy efficiency.
Water and Sanitation
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Provides tap water to rural households.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Focuses on building toilets and waste management systems.
Urban Development
- Affordable Housing: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana has provided homes for millions in urban areas.
- Metro Rail Expansion: Cities like Delhi, Bengaluru, and Kochi benefit from enhanced urban mobility.
Digital Connectivity
- 5G Rollout: India’s 5G network is expected to revolutionize communication and industrial automation.
- Rural Connectivity: BharatNet aims to connect 2.5 lakh gram panchayats with broadband.
Opportunities and Way Forward
Attracting Private Investment
- Encourage private investment in sectors like highways, airports, and power.
- Transparent policies can attract global investors.
Leveraging Technology
- Use of AI, IoT, and blockchain for real-time monitoring and efficiency in project execution.
- Adoption of digital twins in smart city planning.
Sustainable Infrastructure
- Promoting solar parks, wind farms, and EV charging networks.
- Developing eco-friendly transport systems like electric buses and metro rail.
Regional Development and Connectivity
- Strengthening Northeast India’s infrastructure through highways, railways, and waterways.
- Enhancing cross-border connectivity with neighbors like Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan.
Skill Development
- Training workforce in construction, engineering, and project management to meet infrastructure demands.
Case Studies of Successful Infrastructure Projects
Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC)
- Aims to boost industrial development along a 1,500 km corridor.
- Features smart cities, logistics hubs, and high-speed rail.
Kochi Water Metro
- India’s first water metro system ensures sustainable urban mobility.
Bhadla Solar Park
- One of the largest solar parks in the world, contributing to India’s renewable energy goals.
Golden Quadrilateral
- Connects major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata, boosting trade and reducing travel time.
Technological Innovations in Infrastructure
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI-driven predictive analytics optimize construction timelines and costs.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- GIS helps in route planning, land mapping, and disaster management.
Drones
- Used for site surveys, monitoring progress, and ensuring worker safety.
Digital Twins
- Virtual replicas of infrastructure projects for better planning and maintenance.
Critical Issues and Future Outlook
Overlapping Jurisdictions
- Central and state conflicts often delay project execution.
Regulatory Hurdles
- Approvals related to environmental clearances slow down progress.
Corruption
- Leakages in funding and mismanagement increase costs.
Underutilized Assets
- Poor maintenance leads to infrastructure inefficiencies.
Recommendations for Sustainable Growth
Integrated Planning
- Aligning NIP, PM Gati Shakti, and state-level initiatives for holistic development.
Decentralized Governance
- Empowering local bodies to manage urban infrastructure.
Sustainable Practices
- Promoting circular economy principles in construction.
Incentivizing Innovation
- Offering tax benefits for adopting green technologies.
Infrastructure development in India is both a challenge and an opportunity. By addressing funding gaps, leveraging technology, and ensuring sustainable practices, India can transform its infrastructure into a catalyst for economic growth and global competitiveness. With the right policies, investments, and collaborations, India’s infrastructure can pave the way for a brighter, more inclusive future.
Useful Links >>
UPSC Mains Syllabus – General Studies-I: This post provides a detailed breakdown of the General Studies-I syllabus, covering Indian Heritage and Culture, History, and Geography of the World and Society.
Complete Notes of History for UPSC: A comprehensive collection of history notes tailored for UPSC aspirants, encompassing ancient, medieval, and modern Indian history.
UPSC CSE Exam 2025: An Insight: Gain insights into the UPSC Civil Services Examination for 2025, including important dates, exam patterns, and preparation strategies.
Important Books for UPSC Exams: A curated list of essential books recommended for various subjects in the UPSC examination, aiding in effective study planning.
UPSC Prelims Syllabus: An in-depth overview of the UPSC Preliminary Examination syllabus, helping candidates understand the topics to focus on during their preparation.
Practice Questions for UPSC
Prelims Practice Questions
- Delays can stem from administrative factors such as red tape and weak project management.
- Land acquisition challenges can lead to both timeline slippages and cost escalations.
- Environmental opposition is irrelevant once projects are declared part of a national initiative.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- PM Gati Shakti seeks multimodal integration to reduce logistics costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Sagarmala is oriented towards port modernization and connectivity, supporting port-led development and related economic zones.
- Smart Cities Mission is primarily aimed at increasing rural road density to bridge the urban-rural divide.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Frequently Asked Questions
How does infrastructure raise GDP growth beyond just creating construction activity?
Infrastructure raises GDP by improving economy-wide productivity through lower transaction and logistics costs, faster movement of goods, and better reliability of supply chains. It also creates jobs directly and indirectly, while enabling private investment by reducing operational bottlenecks.
Why do funding constraints persist even when policies encourage public-private partnerships (PPPs)?
The article notes that PPPs face delays due to regulatory issues and lack of investor confidence, which weakens timely financial closure and execution. Funding gaps also remain large because the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) projects a very high investment requirement, making mobilization challenging without efficient implementation.
In what ways do land acquisition problems translate into project delays and cost overruns?
Land acquisition often triggers resistance from local communities and involves lengthy approval processes, both of which slow project timelines. These delays raise costs through escalation in material, labor, and financing, and can disrupt coordinated planning across agencies.
What is the link between infrastructure quality and India’s global competitiveness as per the article?
Quality infrastructure improves India’s attractiveness as an investment destination by reducing operational friction and enhancing ease of movement and connectivity. The article also connects robust infrastructure with improved performance in global indices such as Ease of Doing Business and the Global Competitiveness Index.
How do governance issues amplify other infrastructure challenges like delays and environmental concerns?
Coordination challenges among multiple ministries and agencies hinder effective implementation, which can compound delays already caused by red tape and weak project management. Corruption and inefficiency increase costs and can worsen public opposition, especially when projects face ecological damage, deforestation, and displacement concerns.
Source: LearnPro Editorial | Science and Technology | Published: 20 November 2024 | Last updated: 10 March 2026
About LearnPro Editorial Standards
LearnPro editorial content is researched and reviewed by subject matter experts with backgrounds in civil services preparation. Our articles draw from official government sources, NCERT textbooks, standard reference materials, and reputed publications including The Hindu, Indian Express, and PIB.
Content is regularly updated to reflect the latest syllabus changes, exam patterns, and current developments. For corrections or feedback, contact us at admin@learnpro.in.
