Introduction to India’s Foreign Policy
India’s foreign policy is the framework that guides its interactions with the world, emphasizing sovereignty, peace, development, and strategic autonomy. Since gaining independence in 19947, India has sought to balance its regional commitments with global aspirations. Located in a geopolitically strategic position in South Asia, India’s foreign policy focuses on maintaining strong ties with neighbors while forging partnerships with global powers.
This article examines India’s relations with its neighbors and strategic partners, exploring the historical context, key issues, recent developments, challenges, and opportunities.
Historical Evolution of India’s Foreign Policy
Early Years and Non-Alignment (1947-1960s)
- India adopted a Non-Aligned Policy to avoid Cold War rivalries and ensure strategic autonomy.
- Panchsheel Agreement (1954) with China emphasized peaceful coexistence.
- Initial relations with neighbors like Pakistan and Sri Lanka were shaped by territorial and ethnic issues.
Cold War Dynamics and Regional Conflicts (1960s-1990s)
- The Sino-Indian War (1962) marked a turning point, leading to strained relations with China.
- India faced two wars with Pakistan (1965, 1971), with the latter resulting in the liberation of Bangladesh.
- During the Cold War, India leaned towards the Soviet Union for defense and economic support.
Post-Cold War Era and Economic Liberalization (1990s-Present)
- The collapse of the Soviet Union prompted India to diversify its partnerships, especially with the USA and European nations.
- Economic liberalization in 1991 shifted India’s focus toward trade and investment.
- Recent decades have seen India adopt policies like Act East, Neighborhood First, and a proactive stance in multilateral organizations.
Key Principles and Objectives of India’s Foreign Policy
- Strategic Autonomy: Maintaining independence in decision-making while engaging with multiple global powers.
- Non-Alignment 2.0: Adapting the non-aligned approach to modern geopolitical realities.
- Neighborhood First Policy: Strengthening ties with South Asian neighbors for regional stability.
- Act East Policy: Fostering closer ties with ASEAN and East Asia to enhance economic and strategic cooperation.
- Energy and Trade Diplomacy: Ensuring energy security and expanding global trade relations.
- Environmental Leadership: Leading global efforts in combating climate change, as seen through initiatives like the International Solar Alliance.
India’s Relations with its Neighbors
India-Pakistan Relations
- Key Issues:
- Territorial Disputes: Centered around Jammu & Kashmir and the Line of Control (LoC).
- Terrorism: Cross-border terrorism and support for non-state actors remain persistent issues.
- Water Disputes: Sharing of river waters under the Indus Waters Treaty (1960).
- Recent Developments:
- Revocation of Article 370 (2019) heightened tensions, with Pakistan downgrading diplomatic ties.
- Ceasefire agreement along the LoC in 2021 brought temporary relief.
- Future Outlook:
- Backchannel diplomacy and confidence-building measures are essential for peace.
- Trade normalization could pave the way for economic interdependence.
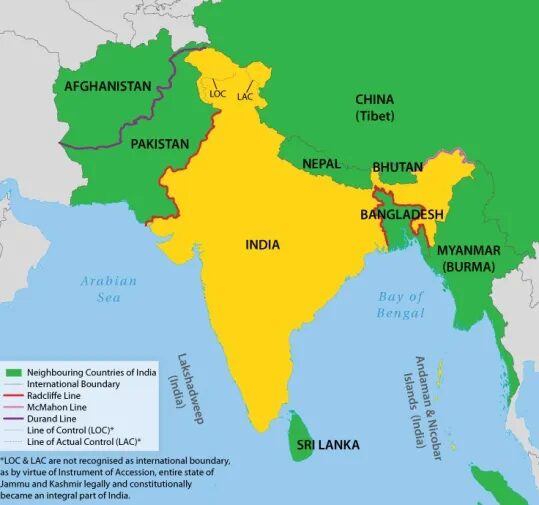
Neighborhood of India
India-China Relations
- Key Issues:
- Border Disputes: The unresolved Line of Actual Control (LAC) has been a source of frequent standoffs.
- Trade Imbalance: India’s imports from China far outweigh its exports, creating economic dependency.
- Strategic Rivalry: Competition in the Indo-Pacific region and global forums like BRICS and SCO.
- Recent Developments:
- The Galwan Valley Clash (2020) marked the most significant border escalation in decades.
- Bilateral trade remains robust, crossing $125 billion in 2021-22 despite tensions.
- Collaborative Areas:
- Climate change, global health, and multilateral institutions offer avenues for cooperation.
India-Nepal Relations
- Key Issues:
- Border Disputes: The Kalapani-Lipulekh issue has strained bilateral ties.
- Chinese Influence: China’s growing investments in Nepal challenge India’s traditional dominance.
- Recent Developments:
- High-level visits and agreements on hydropower projects have strengthened ties.
- India remains Nepal’s largest trading partner and a key provider of development aid.
- Strategic Importance:
- Nepal’s position as a buffer state between India and China underscores its geopolitical significance.
India-Bangladesh Relations
- Key Issues:
- Water Sharing: Disputes over the Teesta River remain unresolved.
- Illegal Immigration: Concerns over undocumented migration from Bangladesh.
- Recent Developments:
- Bilateral trade has grown, with Bangladesh becoming India’s largest trading partner in South Asia.
- Initiatives like the BBIN Motor Vehicle Agreement aim to enhance regional connectivity.
- Opportunities:
- Joint efforts in energy, trade, and disaster management can further strengthen ties.
India-Sri Lanka Relations
- Key Issues:
- Ethnic Tensions: India’s support for Tamil rights has historically been a point of contention.
- Chinese Presence: Projects like the Hambantota Port highlight China’s growing influence.
- Recent Developments:
- India provided critical assistance during Sri Lanka’s economic crisis in 2022.
- Maritime cooperation under the SAGAR Initiative (Security and Growth for All in the Region) has expanded.
- Future Outlook:
- Strengthening economic ties and addressing shared security concerns will be key priorities.
India-Bhutan Relations
- Key Highlights:
- Bhutan’s foreign policy is closely aligned with India due to its historical and cultural ties.
- Hydropower projects like the Tala Dam form the backbone of bilateral economic relations.
- Challenges:
- Growing Chinese influence in Bhutan’s border negotiations.
India-Afghanistan Relations
- Key Issues:
- Political instability following the Taliban’s return to power.
- Concerns over terrorism originating from Afghan soil.
- India’s Role:
- Developmental assistance through projects like the Salma Dam and Zaranj-Delaram Highway.
- Humanitarian aid amid the ongoing crisis.
India’s Relations with Strategic Partners
India-USA Relations
- Key Aspects:
- Defense ties through agreements like LEMOA, COMCASA, and BECA.
- Collaboration in technology, education, and space exploration.
- Shared goals in the Indo-Pacific under the Quad Framework.
- Challenges:
- Trade disputes over tariffs and intellectual property.
- Diverging views on issues like Russia-Ukraine conflict.
India-Russia Relations
- Key Aspects:
- Historical defense cooperation, with India being the largest buyer of Russian arms.
- Energy collaboration, including Arctic exploration and LNG imports.
- Challenges:
- Managing ties with Russia amid growing US-India relations.
- Reducing dependency on Russian military hardware.
India-Japan Relations
- Key Aspects:
- Infrastructure projects like the Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train.
- Collaboration on renewable energy and smart cities.
- Maritime security cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
India-European Union Relations
- Key Aspects:
- Negotiations on the India-EU Free Trade Agreement.
- Partnerships in climate action, green technologies, and digital economy.
India’s Engagement with Multilateral Organizations
United Nations (UN)
- Advocacy for reforms, including India’s permanent membership in the UN Security Council.
G20
- India’s presidency in 2023 emphasized inclusive growth, digital transformation, and climate action.
BRICS
- Promoting economic and technological cooperation among emerging economies.
Quad
- Ensuring a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
Challenges and Opportunities in India’s Foreign Policy
Challenges
- Border Disputes:
- Persistent tensions with China and Pakistan over unresolved borders.
- Geopolitical Shifts:
- Navigating the complexities of US-China-Russia relations.
- Economic Dependencies:
- Trade imbalances with key partners like China.
- Climate Change:
- Addressing shared environmental challenges with regional and global stakeholders.
Opportunities
- Energy Security:
- Diversifying imports and investing in renewable energy partnerships.
- Technological Leadership:
- Collaborating on AI, quantum computing, and space exploration.
- Regional Stability:
- Strengthening the Neighborhood First Policy through trade and connectivity initiatives.
Conclusion
India’s foreign policy is a dynamic blend of realism and idealism, balancing regional responsibilities with global ambitions. By maintaining strong ties with neighbors, fostering strategic partnerships, and actively participating in multilateral platforms, India aims to secure its interests and contribute to global peace and development.
UPSC Exam Relevance
For Prelims
- Focus on key agreements, multilateral organizations, and current developments.
For Mains
- Analytical questions on foreign policy challenges and strategies.
Essay Topics
- Topics like "India’s Role in a Multipolar World" and "Foreign Policy and National Interest."
Interview
- Questions on recent developments and India’s stance on global issues.
Useful Links >>
UPSC Mains Syllabus – General Studies-I: This post provides a detailed breakdown of the General Studies-I syllabus, covering Indian Heritage and Culture, History, and Geography of the World and Society.
Complete Notes of History for UPSC: A comprehensive collection of history notes tailored for UPSC aspirants, encompassing ancient, medieval, and modern Indian history.
UPSC CSE Exam 2025: An Insight: Gain insights into the UPSC Civil Services Examination for 2025, including important dates, exam patterns, and preparation strategies.
Important Books for UPSC Exams: A curated list of essential books recommended for various subjects in the UPSC examination, aiding in effective study planning.
UPSC Prelims Syllabus: An in-depth overview of the UPSC Preliminary Examination syllabus, helping candidates understand the topics to focus on during their preparation.
Practice Questions for UPSC
Prelims Practice Questions
- Economic liberalization shifted India’s external focus toward trade and investment as key priorities.
- Diversifying partnerships after the Soviet Union’s collapse implied exclusive alignment with the USA.
- Policies like ‘Act East’ and ‘Neighborhood First’ reflect a more proactive and regionally anchored diplomacy.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- With Pakistan, confidence-building measures and backchannel diplomacy are highlighted as important for peace and stability.
- With China, unresolved LAC issues coexist with areas of potential cooperation such as climate change and global health.
- With Nepal, India’s role is presented as marginal due to Nepal’s complete dependence on Chinese investments.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Frequently Asked Questions
How does ‘strategic autonomy’ shape India’s engagement with both neighbors and major powers?
Strategic autonomy implies independent decision-making while still engaging multiple global powers on issue-based alignments. It helps India manage regional sensitivities in South Asia while diversifying partnerships in the post-Cold War era without being locked into a single bloc.
What is meant by ‘Non-Alignment 2.0’ in the context of India’s contemporary foreign policy?
Non-Alignment 2.0 refers to adapting the earlier non-aligned approach to present-day geopolitical realities rather than Cold War bloc politics. It emphasizes flexible partnerships, avoiding binary choices, and protecting policy space while pursuing national interests.
Why are India–Pakistan relations described as being affected by a mix of security and resource issues?
The relationship is shaped by territorial disputes around Jammu & Kashmir and the Line of Control, along with persistent concerns of cross-border terrorism. In addition, river-water sharing under the Indus Waters Treaty adds a resource dimension that can intensify political tensions.
How can India simultaneously have border tensions with China and still maintain significant economic engagement?
The article indicates that despite serious border escalation such as the Galwan Valley clash and frequent LAC standoffs, bilateral trade can remain robust due to economic interdependence. However, the trade imbalance also creates concerns about dependency, making the relationship both cooperative and competitive.
Why is Nepal considered strategically important for India’s foreign policy in the neighborhood?
Nepal’s geographic location as a buffer between India and China makes it geopolitically significant. Border disputes like Kalapani-Lipulekh and China’s growing investments add complexity, even as hydropower cooperation and development aid provide avenues to strengthen ties.
Source: LearnPro Editorial | International Relations | Published: 20 November 2024 | Last updated: 10 March 2026
About LearnPro Editorial Standards
LearnPro editorial content is researched and reviewed by subject matter experts with backgrounds in civil services preparation. Our articles draw from official government sources, NCERT textbooks, standard reference materials, and reputed publications including The Hindu, Indian Express, and PIB.
Content is regularly updated to reflect the latest syllabus changes, exam patterns, and current developments. For corrections or feedback, contact us at admin@learnpro.in.
