January 25, 2026 4:29 am
Table of Contents
- Need for Nuclear Power in Kazakhstan:
- 2. Megalithic Burial Excavations Begin in Hanur: Unearthing Iron Age Heritage
- 3. Kazakhstan’s Dry Port Logistics Drive
- 4. ASI Completes Epigraphy Work on Ancient Inscriptions in Thirukurungudi Temples
- 5. Ultrasound-Based Technique: A Revolutionary Approach to Cancer Detection
- 6. Why a Proposed Eco-Sensitive Zone Around Gir Forest is Facing Protests
- 7. Megaprojects and Environmental Challenges: A Look at the Great Nicobar Development Project
- 8. India’s Energy Demand to Triple by 2050: Challenges and Opportunities
- 9. The Significance of Megalithic Burials in India: Unearthing the Iron Age Heritage
- 11. Global Efforts to Save Endangered Vaquita Porpoise
- 12. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Predicting Natural Disasters
1. Kazakhstan Votes on First Nuclear Power Station
Sub: International Relations | Section: Places in News
Context:
Kazakhstan recently held a referendum to decide on constructing its first nuclear power station on the shores of Lake Balkhash. This initiative is crucial for addressing the country’s energy demands while also reducing its reliance on coal-based power generation.

Need for Nuclear Power in Kazakhstan:
- Kazakhstan currently imports much of its electricity from neighboring Russia.
- Domestic power generation facilities are aging, many of which date back to the Soviet era, and are struggling to meet increasing demand.
- Kazakhstan is the world’s largest producer of uranium, accounting for 43% of global supply in 2022.
- Despite its large uranium production, Kazakhstan lacks the infrastructure for uranium enrichment for use as nuclear fuel.
- Building a nuclear power station is aimed at ensuring energy independence while reducing the country’s reliance on coal-based plants and carbon emissions.
Concerns and Public Opposition:
- Public concerns are rooted in Kazakhstan’s history with nuclear testing during the Soviet era, particularly in the Semipalatinsk region.
- Between 1949 and 1989, approximately 450 nuclear tests were conducted in Kazakhstan, exposing around 1.5 million people to radiation, which has caused long-term health issues.
- Fears of nuclear accidents are prominent, with references to the Chornobyl disaster highlighting the risks involved in nuclear energy production.
- Skepticism also surrounds Russia’s involvement in the project, as critics argue this could limit Kazakhstan’s sovereignty over its energy sector.
Referendum and Public Participation:
- A referendum is a direct vote by an electorate on an important issue or proposal.
- The referendum on the nuclear power station allowed citizens to express whether they wanted such a project in their country.
- Referendums are often used for major issues such as infrastructure projects, constitutional amendments, or policy reforms.
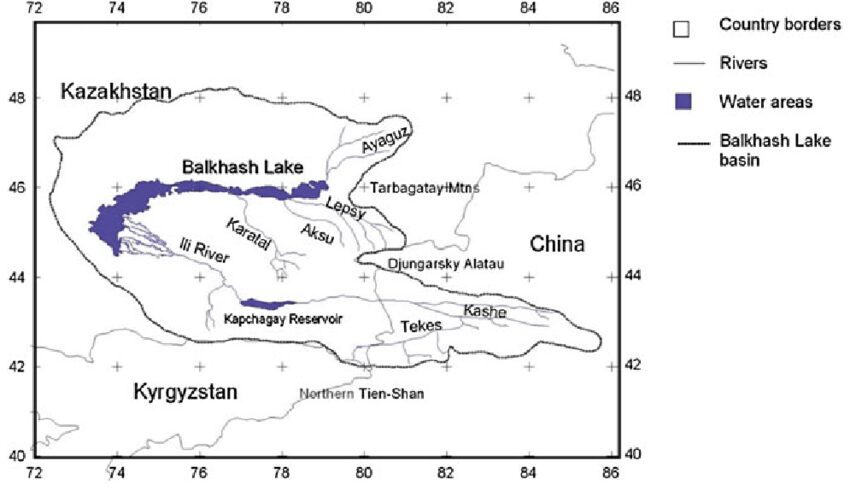
Lake Balkhash:
- Lake Balkhash is one of the largest lakes in Central Asia and is a key geographical feature in Kazakhstan.
- It is an endorheic lake, meaning it doesn’t drain into any ocean. The western half of the lake contains freshwater, while the eastern half contains saline water.
- The lake faces environmental challenges, including shrinking and increasing salinity, which threatens the ecosystem and water resources.
Global Nuclear Energy Context:
- Countries such as France, Japan, and the United States heavily rely on nuclear power to meet their energy demands.
- China and India have been expanding their nuclear energy capabilities rapidly in recent years.
- Nuclear energy is considered a low-carbon solution to energy generation, which is vital in efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- However, nuclear energy also presents challenges, such as waste disposal, the risk of nuclear accidents, and concerns over the proliferation of nuclear weapons.
| Do You Know? | Kazakhstan is the world’s largest uranium producer, providing 43% of the global supply as of 2022. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | Kazakhstan’s Semipalatinsk region was the site of 450 nuclear tests during the Soviet era, making it one of the most heavily irradiated regions in the world. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Kazakhstan is a landlocked country located in Central Asia. 2. Lake Balkhash is an endorheic lake, with half freshwater and half saline waters. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The impact of nuclear energy as a low-carbon option to address global energy challenges. 2. Kazakhstan’s potential role as a nuclear energy producer and the socio-political implications of this shift. |
| Relevance | The topic is relevant for questions on energy independence, international cooperation, nuclear energy development, and environmental issues linked to energy production. |
2. Megalithic Burial Excavations Begin in Hanur: Unearthing Iron Age Heritage
Sub: History | Section: Ancient History
Context:
Excavations have commenced at a significant megalithic burial site in Doddalathur village, located in Hanur taluk of Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka. This excavation is a joint initiative led by the University of Mysore and the Mythic Society, Bengaluru, aiming to uncover the rich Iron Age heritage of South India. The project also serves as a training ground for archaeology students.
About Excavation Site:
- The excavation is taking place in Doddalathur village, located in a valley formed by the Male Mahadeshwara Hill ranges in Hanur taluk, Karnataka.
- The site is believed to date back to the Megalithic Period or Iron Age, roughly between 1200 BCE and 300 CE in South India.
- The village once had over 1,000 megalithic burials, but many have been disturbed or destroyed due to agricultural expansion, settlement, and land development.
Megalithic Culture:
- The term “Megalith” comes from the Greek words “mega” (large) and “lithos” (stone), indicating large stone structures, often associated with burials.
- Megalithic culture refers to the use of large stones for burial practices and monuments.
- These burials often signify social complexity, with stone circles, dolmens, cairns, and capstones marking graves.
- Megaliths are prevalent in Peninsular India, especially in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh.
Types of Megaliths:
- Menhirs: Single standing stones, often for commemorative or religious purposes.
- Dolmens: Table-like structures formed by large flat stones placed atop upright stones, used for burials.
- Cairns: Heaps or piles of stones marking graves.
- Stone Circles: Circular stone arrangements around burial sites.
- Cist: A small stone coffin used to hold the remains of the dead.
Iron Age and Settlement Patterns:
- The Iron Age marked the use of iron tools and weapons, leading to advances in agriculture, warfare, and settlements.
- Megalithic burials often used large boulders (megaliths) in circular patterns, indicating complex burial practices.
- Iron Age settlements were located in fertile valleys and hilly regions (e.g., Male Mahadeshwara Hills).
| Do You Know? | The term “Megalith” refers to large stone structures, often used in burial practices, dating back to before 3000 BCE in India. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | Megalithic burials in Southern India are often associated with the Iron Age and signify complex burial rituals and social stratification. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. The Megalithic Period in South India is believed to be between 1200 BCE and 300 CE. 2. Megaliths can be found extensively in Peninsular India, especially in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The significance of megalithic burials in understanding Iron Age cultures. 2. How agricultural expansion and modern development have threatened archaeological sites. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on archaeology, Iron Age India, and South Indian historical practices. |
3. Kazakhstan’s Dry Port Logistics Drive
Sub: Geography | Section: Economic Geography
Context:
Kazakhstan is focusing on developing a dry port logistics network to improve its trade and transportation capabilities. This initiative is critical for enhancing the country’s export potential and facilitating regional economic integration, particularly with the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) led by China.
What is a Dry Port?
- A dry port is an inland terminal connected to a seaport by road or rail, where importers and exporters can handle customs clearance, storage, and consolidation of goods.
- These ports relieve congestion at seaports by managing freight traffic further inland.
- They are important hubs for landlocked countries like Kazakhstan, as they facilitate efficient and cost-effective trade by reducing the reliance on coastal ports.
Importance of Dry Ports for Kazakhstan:
- Kazakhstan is a landlocked country, sharing borders with Russia, China, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan.
- It has no direct access to oceans, making dry ports essential for international trade.
- Dry ports in Kazakhstan serve as critical links to major trade routes, including China’s Belt and Road Initiative, connecting Asia to Europe.
- Export Potential: Dry ports help Kazakhstan boost its export sectors, including energy, minerals, and agricultural products.
Kazakhstan’s Government Initiatives:
- Kazakhstan’s Northern Corridor, which connects China and Europe, is being developed as a major logistics hub, with the government pushing for public-private partnerships (PPP) to build and manage new dry ports.
- The government has prioritized infrastructure development for multi-modal transport systems, integrating road, rail, and seaports to streamline trade.
Existing Dry Port Infrastructure:
- Kazakhstan’s dry ports are strategically located near its major trade partners, including Russia, China, and the European Union.
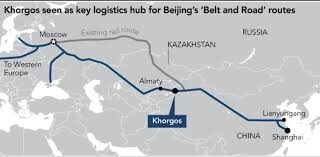
- Khorgos Gateway: Located on the border with China, it is one of the largest dry ports in the world and a key point along the New Silk Road.
- The dry ports provide container handling and warehousing facilities, improving the efficiency of transcontinental trade.
Challenges in Dry Port Development:
- Geopolitical Risks: Kazakhstan’s location between major powers like Russia and China presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of political influence and competition.
- Cost and Infrastructure: Developing a robust dry port network requires substantial investments in infrastructure, including railways, highways, and customs facilities.
- Climate and Geography: The harsh climate and vast geographical distances pose logistical challenges, particularly in winter months.
Regional Connectivity and BRI:
- Kazakhstan’s dry ports play a crucial role in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), connecting East Asia to Europe through Central Asia.
- Rail Freight: Rail is becoming an increasingly popular method for moving goods between China and Europe via Kazakhstan, as it is faster than sea transport.
- The BRI infrastructure projects have transformed Kazakhstan into a regional logistics hub.
| Do You Know? | Kazakhstan’s Khorgos Gateway dry port is one of the largest in the world and a critical hub for the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | Kazakhstan is a landlocked country with one of the world’s largest inland dry ports, playing a key role in transcontinental trade. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Kazakhstan shares borders with Russia, China, and four Central Asian countries. 2. A dry port is an inland terminal connected to a seaport by road or rail. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The importance of dry ports in facilitating international trade for landlocked countries. 2. How Kazakhstan’s role in the Belt and Road Initiative boosts its global trade significance. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on regional trade, logistics infrastructure, and economic geography in Central Asia. |
4. ASI Completes Epigraphy Work on Ancient Inscriptions in Thirukurungudi Temples
Sub: History | Section: Medieval History
Context:
The Epigraphy Division of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has recently completed a detailed estampage of ancient inscriptions found in the temples of Thirukurungudi, located in Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu. These inscriptions offer insights into the political, social, and religious history of the Pandya and Vijayanagara periods.

Temples Involved:
- The epigraphy work was conducted in three significant temples:
- Nambi Rayar Temple
- Thirumalai Nambi Temple
- Aniliswarar Temple
Significance of Inscriptions:
- Inscriptions serve as valuable historical records, detailing land grants, donations to temples, and important political events.
- Inscriptions from these temples date back to the Pandya and Vijayanagara periods, revealing insights into local governance, religious practices, and temple administration.
Estampage Method:
- Estampage is a technique used by archaeologists to make precise copies of inscriptions on stone or metal surfaces.
- Process:
- The surface of the inscribed stone is thoroughly cleaned.
- A maplitho paper is pressed onto the surface to capture the engravings.
- Ink is applied after the paper dries to highlight the inscription.
- The estampage can be stored for analysis and serves as a permanent record of the inscription.
Key Inscriptions Found:
- The Nambi Rayar Temple inscriptions describe land donations given for maintaining flower gardens and supporting temple rituals.
- Thirumalai Nambi Temple inscriptions detail community involvement in temple activities and religious festivals.
- The Aniliswarar Temple contains Pandya-era inscriptions written in Vattezhuthu script, mentioning donations like ghee for perpetual lamps in the temple.
Historical Context:
- Pandya Dynasty:
- The Pandya dynasty ruled southern India from the 6th century BCE to the 14th century CE.
- Their capital was Madurai, and they were known for building magnificent temples, including the Meenakshi Temple.
- Vijayanagara Empire:
- Founded in 1336 CE, the Vijayanagara Empire lasted until the 17th century.
- Known for its prosperity, trade, and temple architecture, the empire played a key role in defending southern India from Islamic invasions.
Contributions of ASI:
- The Archaeological Survey of India has been instrumental in preserving these inscriptions and documenting the history of temple architecture, rituals, and governance.
- The epigraphy work helps historians better understand the temple culture, religious endowments, and the social structure of medieval South India.
| Do You Know? | The Pandya dynasty is one of the oldest ruling dynasties in India, with references dating back to the 6th century BCE. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | The estampage method used by the ASI involves creating a permanent record of inscriptions using paper, ink, and careful impressions. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Vijayanagara Empire was founded in 1336 CE and lasted until 1646 CE. 2. The Pandya dynasty had its capital at Madurai. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The importance of epigraphy in understanding medieval Indian history. 2. The role of temples as centers of religious and social life during the Pandya and Vijayanagara periods. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on Indian history, medieval inscriptions, and temple culture in southern India. |
5. Ultrasound-Based Technique: A Revolutionary Approach to Cancer Detection
Sub: Science | Section: Health
Context:
A new ultrasound-based method for detecting cancers is being developed by scientists. This non-invasive technique could potentially replace biopsy procedures, which are currently the standard for diagnosing cancers. This groundbreaking innovation was recently presented at the joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and the Canadian Acoustical Association.
What is Ultrasound-Based Cancer Detection?
- This novel method uses high-frequency ultrasound to detect cancerous tissues in the body.
- Ultrasound waves break off small tissue fragments from potentially cancerous areas, which are then analyzed for biomarkers like RNA, DNA, and proteins.
- The technique enhances the concentration of these biomarkers in the bloodstream, which can then be tested for early detection of cancer.
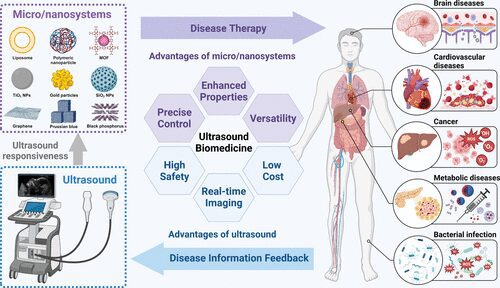
How it Works:
- High-energy ultrasound waves are directed at suspected areas of cancer.
- These waves cause small tissue fragments to release genetic material and proteins into the bloodstream.
- The increased concentration of these biomarkers improves the accuracy of cancer detection and reduces the need for invasive procedures like biopsies.
Advantages of Ultrasound Technology:
- Non-invasive: Unlike traditional biopsy, this method doesn’t require tissue samples to be physically removed, making it less risky and less painful.
- Radiation-free: Ultrasound technology does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option, especially for frequent screenings.
- Detailed Imaging: Ultrasound provides detailed images of soft tissues, making it useful for detecting cancers in organs like the breast, prostate, and liver.
Additional Innovations in Ultrasound Cancer Detection:
- Photoacoustic Imaging: This new imaging method combines laser technology with ultrasound to create high-resolution images of blood vessels around tumors.
- The technology captures images up to 1,000 times faster than previous systems, allowing for quicker diagnosis.
- Wearable Ultrasound Devices: Miniaturized ultrasound devices have been developed that allow patients, particularly women, to perform breast imaging at home.
- These devices can detect tumors as small as 0.3 cm, potentially improving early detection rates.
Future Prospects:
- The U.S. National Cancer Institute has launched the Cancer Screening Research Network, aiming to explore cutting-edge cancer detection methods, including ultrasound-based screening.
- Large-scale clinical trials are expected by 2025, involving 24,000 participants to validate the effectiveness of this method.
Limitations and Challenges:
- While this method shows promise, further research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness across various cancer types.
- There may be challenges in differentiating between benign and malignant tumors, a critical aspect of cancer diagnosis.
| Do You Know? | Ultrasound technology has been widely used in medical diagnostics for decades, but recent innovations are bringing it into cancer detection. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | Photoacoustic imaging combines laser and ultrasound technology to create high-resolution images, making it easier to detect cancerous tissues. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that does not use ionizing radiation. 2. Photoacoustic imaging is an emerging cancer detection method that uses laser-generated sound waves. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The advantages of non-invasive diagnostic technologies in healthcare. 2. The role of ultrasound technology in improving early cancer detection and reducing the need for biopsies. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on health technology innovations, non-invasive diagnostic tools, and the future of cancer detection. |
6. Why a Proposed Eco-Sensitive Zone Around Gir Forest is Facing Protests
Sub: Environment | Section: Protected Areas
Context:
The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) proposed creating an Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) around Gir Forest, Gujarat. Initially proposed to cover 3,328 sq km, the area was later reduced to 2,061 sq km after considering local concerns. Despite this adjustment, the proposal has sparked protests from farmers and local businesses.
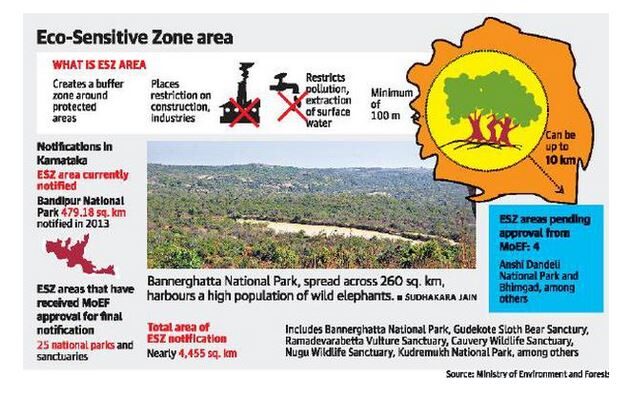
What is an Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ)?
- Eco-Sensitive Zones are buffer areas around national parks and wildlife sanctuaries meant to protect biodiversity by regulating certain human activities.
- Activities like commercial mining, polluting industries, and tree felling are either prohibited or regulated in these zones.
- The main objective is to reduce the human impact on the core areas of protected ecosystems.
Reasons for Protests:
- Farmers: Local farmers argue that the restrictions imposed by the ESZ will prevent them from protecting their crops from wildlife, especially Asiatic lions.
- Businesses: Tourism and hospitality businesses fear that limitations on new resorts and commercial enterprises will hurt local industries, particularly those dependent on visitors to Gir National Park.
- Livelihoods: Many small-scale industries and farmers depend on resources near the forest, and fear that the ESZ will limit their access to these resources.

Previous Disputes Over the ESZ:
- A similar proposal in 2016 led to protests, as local communities expressed concerns about their rights to self-defense against wildlife attacks. The government then reduced the ESZ area to 1,114 sq km.
- This revised area was later challenged in court, and the Gujarat High Court has since put the notification on hold pending further review.
Gir Forest’s Unique Biodiversity:
- Gir National Park is the last remaining habitat of the Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica), which has seen its population grow from 327 in 2001 to 674 in 2020 due to concerted conservation efforts.
- The park also supports leopards, hyenas, deer, and a variety of bird species, making it an important area for wildlife conservation.
Process of Declaring an ESZ:
- State governments submit ESZ proposals to the MoEFCC for approval.
- The ministry issues a draft notification, inviting public comments within 60 days.
- After reviewing suggestions from the public and the state, the ministry finalizes the notification based on recommendations from an expert committee.
Activities Regulated in an ESZ:
- Prohibited Activities: Commercial mining, industrial pollution, deforestation, etc.
- Regulated Activities: Tourism activities, tree felling, and expansion of industries.
- Permitted Activities: Agriculture, organic farming, use of renewable energy sources, and eco-friendly tourism.
Challenges for Local Communities:
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Many farmers near Gir Forest face frequent issues with lions preying on livestock and damaging crops.
- Economic Impact: Tourism is a major source of revenue for the region, and any restrictions on infrastructure development may hurt local businesses.
Asiatic Lion Conservation:
- The Asiatic lion is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, and Gir Forest is its only surviving natural habitat.
- Conservation efforts, including anti-poaching measures and local community involvement, have played a key role in stabilizing and increasing the lion population.
| Do You Know? | The Asiatic lion is slightly smaller than its African counterpart and has a distinctive fold of skin along its belly. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | Gir Forest is the only place in the world where Asiatic lions live in the wild, making it a unique conservation area. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) act as buffers around protected areas to regulate human activities. 2. The Asiatic lion is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The role of Eco-Sensitive Zones in protecting biodiversity. 2. The challenges of balancing wildlife conservation with the livelihoods of local communities. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on biodiversity conservation, protected areas, and environmental policies. |
7. Megaprojects and Environmental Challenges: A Look at the Great Nicobar Development Project
Sub: Geography | Section: Human Geography
Context:
The Great Nicobar Development Project has sparked concerns over its potential impact on local ecosystems and the Shompen tribe, one of the most isolated tribal groups in the world. The project involves building a transshipment port, an airport, and other infrastructure on Great Nicobar Island, raising questions about balancing development with environmental conservation and indigenous rights.

Key Components of the Great Nicobar Development Project:
- International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT): This will be a key feature of the project, positioning the island as a critical hub for global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: A new airport is planned for both military and civilian use, enhancing the island’s connectivity.
- Power Plant: To support the new infrastructure, a power plant will be constructed, raising concerns about the island’s already fragile ecosystem.
- Tourism Infrastructure: Roads, public transport, and hotel developments are being planned to boost tourism, though these are likely to disrupt local biodiversity.
Environmental Impact:
- The project will require the diversion of 130 sq km of forests and the felling of 9.64 lakh trees, threatening the island’s rich biodiversity.
- Great Nicobar is home to several endangered species, including the Giant Leatherback Turtle, Nicobar Megapode, and Nicobar Tree Shrew.
- The island’s forests and coastal ecosystems play a crucial role in carbon sequestration and serve as natural defense mechanisms against tsunamis and storm surges.
Impact on the Shompen Tribe:
- The Shompen tribe is a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) that has lived on the island for over 60,000 years.
- The tribe is semi-nomadic, relying on hunting, fishing, and gathering for their survival. The project’s infrastructure could severely disrupt their way of life.
- The Shompen have minimal contact with the outside world, and their numbers are estimated to be around 229 as per the 2011 Census. Any major development could threaten their cultural identity and survival.
Concerns Over the Project:
- Biodiversity Loss: With large-scale deforestation, the project is expected to have a severe impact on endemic species and ecosystems.
- Climate Change: The island is particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels and extreme weather events, both of which could be exacerbated by the destruction of its natural defenses.
- Human Rights: Activists and environmentalists have raised concerns about the rights of the Shompen and Nicobarese tribes, calling for a review of the project’s environmental and social impacts.
Development vs. Conservation Debate:
- Supporters argue that the project will bring much-needed economic growth to the region, positioning India as a key player in global maritime trade.
- Critics point out that the loss of biodiversity and indigenous rights are too great a price to pay for development.
- Sustainability measures, such as environmental impact assessments (EIAs), have been conducted, but many argue that these are insufficient to protect the island’s unique ecosystems and communities.
| Do You Know? | The Shompen tribe is one of the most isolated communities in the world, with little to no contact with the outside world. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | Great Nicobar Island is home to the Giant Leatherback Turtle, one of the largest sea turtles in the world, which uses the island’s beaches for nesting. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Great Nicobar Island is part of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. 2. The Shompen tribe is classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG). |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The role of infrastructure projects in economic development and their environmental impacts. 2. The challenges of balancing indigenous rights and biodiversity conservation in large development projects. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on human geography, environmental sustainability, and the impact of megaprojects on indigenous communities. |
8. India’s Energy Demand to Triple by 2050: Challenges and Opportunities
Sub: Economics | Section: Infrastructure
Context:
India’s energy demand is expected to triple by 2050, driven by rapid economic growth and urbanization. As the third-largest power market in the world, India is positioning itself as a key player in the global energy transition. However, meeting this growing demand while reducing carbon emissions presents significant challenges.
India’s Energy Scenario:
- GDP Growth: India’s GDP is currently growing at 7%, leading to an 8% rise in power demand this year alone.
- Energy Mix: Despite significant investments in renewables, coal still accounts for 70% of India’s power generation.
- Renewable Energy Targets: By 2030, India aims to have 200 GW of solar and wind capacity, positioning itself as a global leader in clean energy.
Global Role in Energy Transition:
- India is now the second-largest manufacturer of solar modules, exporting to key global markets.
- It is also a critical player in the shift toward low-carbon economies, with plans to increase battery storage capacity and electric vehicle production.
- However, energy storage, grid infrastructure, and the pace of renewable energy deployment remain key challenges.
Challenges in Meeting Energy Demand:
- Energy Storage: The intermittency of renewables like solar and wind makes battery energy storage systems (BESS) critical for maintaining grid stability.
- Infrastructure Development: India’s energy infrastructure, especially in rural areas, needs significant upgrades to accommodate the growing demand.
- Coal Dependency: Although renewables are growing, India’s reliance on coal will likely continue for the foreseeable future. By 2030, India will still have around 50 GW of coal capacity.
Government Initiatives:
- The Ministry of Heavy Industries launched the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme in 2021 to support the manufacture of advanced chemistry cell (ACC) battery storage, targeting 50 GWh of storage capacity.
- The Viability Gap Funding (VGF) scheme for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) aims to reduce storage costs and make renewable energy more competitive.
Electric Mobility in India:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): The EV market is growing rapidly, with major automakers establishing battery assembly plants.
- Lithium-ion Battery Demand: Demand for lithium-ion batteries is expected to rise from 10 GWh to 200 GWh by 2035.
- Battery Production: By 2030, India’s battery production capacity is expected to reach 150 GWh, covering 13% of total cell demand.
| Do You Know? | India has become the second-largest manufacturer of solar modules in the world, supplying key global markets. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | India aims to generate over 200 GW from solar and wind by 2030, making it a leader in the renewable energy sector. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. India’s energy demand is expected to triple by 2050. 2. The Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme promotes the manufacture of advanced chemistry cell (ACC) battery storage. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The challenges and opportunities in energy infrastructure development. 2. India’s role in the global energy transition and its approach to balancing coal and renewable energy. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on energy security, infrastructure development, and the global shift toward low-carbon economies. |
9. The Significance of Megalithic Burials in India: Unearthing the Iron Age Heritage
Sub: History | Section: Ancient History
Context:
The excavation of a significant megalithic burial site in Doddalathur village, Karnataka, has provided new insights into Iron Age culture in South India. Led by the University of Mysore and the Mythic Society, this project aims to uncover the region’s archaeological heritage while serving as a training ground for archaeology students.
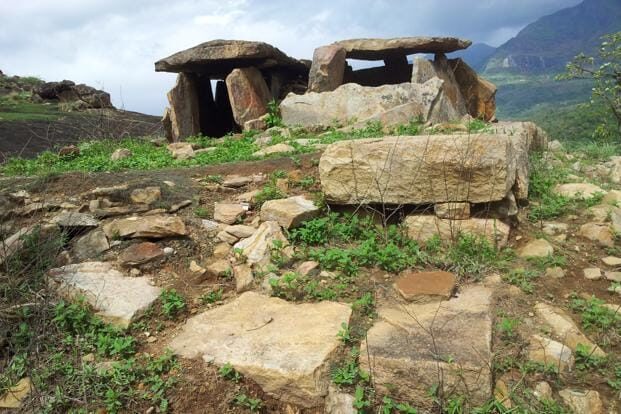

What are Megalithic Burials?
- Megalithic burials are large stone structures associated with burial practices during the Iron Age in India, dating between 1200 BCE and 300 CE.
- These structures include menhirs, dolmens, cairns, and stone circles, which were used to commemorate the dead or mark burial sites.
Key Features of the Excavation:
- The excavation is taking place in Doddalathur village, located near the Male Mahadeshwara Hill ranges in Chamarajanagar district, Karnataka.
- The site was first discovered in 1961 by C. Krishnamurti of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- The region was once home to over 1,000 megalithic burials, though many have been destroyed due to agriculture and land development.
Types of Megaliths in India:
- Menhirs: Single-standing stones erected to mark burial sites or commemorate events.
- Dolmens: Table-like structures with a large flat stone placed on upright stones, typically used as burial chambers.
- Cairns: Stone heaps or piles used as grave markers.
- Stone Circles: Circular arrangements of stones around burial sites, often indicating ritual significance.
Significance of the Excavation:
- The Iron Age in India was characterized by the use of iron tools and weapons, leading to advancements in agriculture, warfare, and settlement development.
- Megalithic burials offer insights into social structures, religious practices, and the importance of death rituals in ancient Indian communities.
Past Excavations in the Region:
- In 2021 and 2022, the Department of Ancient History and Archaeology conducted excavations at Budipadaga, a site located 20 km southwest of Doddalathur, revealing similar Iron Age artifacts and burials.
| Do You Know? | Megalithic culture refers to the use of large stones for burial and commemorative practices, dating back over 3,000 years. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | Megaliths have been discovered across peninsular India, particularly in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Megalithic burials are associated with the Iron Age in India. 2. The site at Doddalathur dates back to around 1200 BCE to 300 CE. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The significance of megalithic burials in understanding ancient Indian society. 2. How archaeological excavations contribute to our knowledge of the Iron Age in South India. |
| Relevance | Relevant for questions on archaeological discoveries, Iron Age culture, and the use of megaliths in ancient burial practices. |
11. Global Efforts to Save Endangered Vaquita Porpoise
Sub: Environment | Section: Species in News
Context:
The vaquita porpoise (Phocoena sinus), the world’s most endangered marine mammal, is on the verge of extinction, with fewer than 10 individuals remaining. Conservationists and governments are making last-ditch efforts to save this species from disappearing.
About the Vaquita Porpoise:
- The vaquita is a small porpoise native to the northern part of the Gulf of California, Mexico.
- It has been listed as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- The vaquita population has drastically declined due to bycatch in illegal gillnet fishing, particularly for the totoaba fish, whose swim bladders are highly valued in the black market.
Causes of Decline:
- Illegal Totoaba Fishing: The totoaba’s swim bladder is considered a delicacy and is used in traditional Chinese medicine. Fishermen use gillnets to catch the totoaba, but these nets also trap vaquitas.
- Habitat Destruction: Pollution and habitat degradation in the Gulf of California have further contributed to the declining population.
Conservation Efforts:
- Gillnet Bans: The Mexican government has banned gillnet fishing in the vaquita’s habitat, although enforcement remains a challenge.
- International Cooperation: Environmental organizations, such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and Sea Shepherd Conservation Society, are working with the Mexican government to patrol the Gulf of California and remove illegal gillnets.
- VaquitaCPR Program: This program involves capturing remaining vaquitas and placing them in a protected sanctuary to prevent accidental entrapment in fishing gear.
Challenges to Conservation:
- Lack of Enforcement: Although the Mexican government has banned gillnets, enforcement is inconsistent, and poaching remains a significant threat.
- Public Awareness: There is limited awareness among the global population about the vaquita’s plight, reducing international pressure to take urgent actions.
Future Outlook:
- Technological Solutions: Conservationists are developing alternative fishing gear that is safe for vaquitas but effective for catching legal fish species. These nets could help fishermen transition away from gillnets without economic loss.
- Population Recovery: Experts argue that saving the species will require more aggressive enforcement and perhaps even relocating the remaining individuals to safer areas for breeding and monitoring.
| Do You Know? | The vaquita is the smallest cetacean in the world, measuring around 4-5 feet in length. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | The vaquita was only discovered in 1958, making it one of the most recently identified marine mammals. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. Vaquita porpoises are found exclusively in the Gulf of California, Mexico. 2. They are critically endangered, with fewer than 10 individuals left. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The impact of illegal fishing practices on marine biodiversity. 2. Challenges faced by marine conservation efforts in enforcing regulations and international cooperation. |
| Relevance | Relevant for discussions on endangered species, conservation strategies, and environmental protection laws. |
12. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Predicting Natural Disasters
Sub: Science & Technology | Section: Disaster Management
Context:
As climate change intensifies natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, governments and scientific institutions are increasingly turning to Artificial Intelligence (AI) to improve predictive models and mitigate the impacts of these disasters.
How AI Helps Predict Natural Disasters:
- AI systems analyze vast amounts of satellite data, weather patterns, and historical data to detect early signs of natural disasters.
- Machine learning algorithms identify anomalies in weather systems or seismic activity that could indicate an impending disaster, providing faster and more accurate warnings.
- AI can forecast flood levels, tsunami trajectories, and hurricane paths by analyzing water levels, atmospheric conditions, and wind speeds, helping authorities to prepare.
Types of Natural Disasters Predicted by AI:
- Earthquakes: AI tools can analyze real-time seismic data, enhancing earthquake early warning systems and helping in the quick deployment of emergency responses.
- Hurricanes: AI-driven models help forecast hurricane intensity and landfall timing, allowing better evacuation planning and risk management.
- Floods: Predictive models can estimate where flooding will occur based on rainfall, soil moisture levels, and river flow rates, helping to create flood maps that guide rescue operations.
- Forest Fires: AI can analyze weather conditions, vegetation dryness, and wind patterns to predict the likelihood of wildfires, enabling preemptive evacuation efforts.
Recent Applications of AI in Disaster Management:
- Google’s Flood Forecasting Initiative: Using AI, Google has been able to accurately predict floods in India and Bangladesh by analyzing water levels and historical flood patterns.
- AI in Earthquake Prediction: In Japan, AI systems are being used to monitor tectonic movements and send alerts to residents ahead of potential earthquakes.
- Wildfire Prediction in the USA: AI is being used in California to predict where wildfires are most likely to start and spread, reducing the time needed to deploy firefighting resources.
Challenges in Implementing AI for Disaster Prediction:
- Data Quality: Accurate AI predictions require comprehensive and reliable data, which may not always be available, especially in remote areas.
- Computational Power: Predicting large-scale natural disasters requires significant computational resources, which are costly and not always accessible to developing countries.
- Ethical Concerns: There are concerns about privacy, data security, and the potential misuse of AI systems for purposes other than disaster prevention.
Future Outlook:
- AI and Climate Change: As the frequency and intensity of natural disasters increase due to climate change, AI will play a crucial role in improving climate resilience and disaster management.
- Collaboration: Global collaboration between governments, tech companies, and research institutions is essential to improve the accuracy and availability of AI-powered disaster prediction tools.
| Do You Know? | Google’s Flood Forecasting Initiative has been able to provide flood predictions up to 48 hours in advance in some regions. |
|---|---|
| Interesting Fact | AI is being used to create fire spread maps in California, helping firefighters combat wildfires more effectively. |
| Facts for Prelims Exam | 1. AI is widely used in disaster management to predict events like earthquakes, floods, and wildfires. 2. Google’s AI-based flood forecasting has been particularly successful in South Asia. |
| Facts for Mains Exam | 1. The role of technology in disaster preparedness and mitigation. 2. Challenges and ethical concerns in the use of AI for disaster prediction. |
| Relevance | This topic is relevant for science and technology, disaster management, and climate change adaptation strategies in both prelims and mains exams. |


