January 25, 2026 7:46 am
Table of Contents
- 1. Shompen Tribe of Nicobar
- 2. Use of Salt Pan Land for Housing: Ecological and Urban Planning Concerns in Mumbai
- 3. Halari Donkeys: Brains and Brawn in Gujarat
- 4. Revitalization of the Six-Decade-Old Canal System of Hirakud Dam
- 5. India’s Energy Demand to Triple by 2050
- 6. Anti-Cancer Drugs to Sport QR Codes to Check Fakes
- 7. Two Months On, Meghalaya Polio Case Shrouded in Secrecy
- 8. World Bank Mulls 27 of 30 Ideas on MDBs by G20 Independent Group
- 9. What’s Behind Israel’s Ban on the UN Chief?
- 10. Revitalization of India's Electric Mobility Sector
- 11. Israel’s Military and Civilian Dual-use Port in Great Nicobar
1. Shompen Tribe of Nicobar
Sub: Geography | Section: Human Geography
Why in News:
The Shompen tribe of the Nicobar Islands has come into the spotlight due to concerns over a major infrastructure project on Great Nicobar Island, which threatens their forest home. The project includes a transshipment container terminal, port, and solar power plant, raising environmental and anthropological concerns.

About Shompen Tribe:
The Shompen tribe is a semi-nomadic, forest-dwelling community that has inhabited the Great Nicobar Island for over 60,000 years. Unlike the coastal Nicobarese tribe, the Shompen live in the island’s interior, relying heavily on the forest for their sustenance.
- They are one of the most isolated Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India.
- Semi-nomadic hunter-gatherers, they rely on hunting, gathering, fishing, and rudimentary horticulture.
- Their staple food is the pandanus fruit, and they speak their own language, often unintelligible even between bands.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The Shompen tribe is one of the least studied tribes in India, with much of their population still uncontacted by the outside world. |
| Background | The Shompen tribe has lived in isolation for over 60,000 years, largely avoiding interaction with the outside world. |
| Interesting Fact | The exact population of the Shompen is unknown, although the 2011 Census estimates it to be around 229. |
| Relevance | This issue is important for understanding the challenges of infrastructure development vs. tribal rights and environmental preservation in India’s remotest regions. |
2. Use of Salt Pan Land for Housing: Ecological and Urban Planning Concerns in Mumbai
Sub: Geography | Section: Economic Geography
Why in News:
The Maharashtra government has allocated 255.9 acres of salt pan land in Mumbai’s eastern suburbs for the construction of rental housing as part of the Dharavi Redevelopment Project. Environmentalists have raised concerns about the impact of converting salt pan land, which serves as natural flood defenses.

What are Salt Pan Lands?
Salt pans are low-lying lands where seawater flows in and evaporates, leaving behind salt and minerals. They play an essential role in the ecosystem by acting as natural flood buffers.
- Mumbai has 5,378 acres of salt pan land.
- Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) laws restrict development on salt pans.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Salt pans, along with mangroves, serve as critical natural flood barriers for coastal cities like Mumbai. |
| Background | Salt pans are ecologically sensitive areas, falling under CRZ-1B regulations, where most development is restricted. |
| Interesting Fact | Across India, 60,000 acres of land are classified as salt pans, with Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu holding the largest shares. |
| Relevance | Understanding the conflict between urbanization, environmental preservation, and sustainable development is crucial for planning and geography topics. |
3. Halari Donkeys: Brains and Brawn in Gujarat
Sub: Environment | Section: Species in News

Context:
The Halari donkey, an endangered breed found in the Halar region of Gujarat, has become a key focus for conservation efforts. With fewer than 500 Halari donkeys remaining, they are prized for their strength, intelligence, and economic value, including their highly sought-after milk.
Uses and Economic Value:
The Halari donkey has long been used to carry heavy loads in building dams, forts, hilltop temples, and for pottery work. The price of a Halari donkey now exceeds ₹1 lakh due to rising demand for its milk, which is used in cosmetics and sold for over ₹7,000 per kg in powdered form.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Halari donkey milk is prized for its sweetness and is in high demand in cosmetic industries, both domestically and internationally. |
| Background | The Sahjeevan Trust is collaborating with Gujarat’s Animal Husbandry Department to conserve the breed through selective breeding programs. |
| Interesting Fact | Halari donkeys have been used for centuries by the Bharwad and Rabari pastoralists during their seasonal migrations. |
| Relevance | The conservation of indigenous livestock breeds like the Halari donkey is essential for topics related to biodiversity and rural livelihoods. |
4. Revitalization of the Six-Decade-Old Canal System of Hirakud Dam
Sub: Geography | Section: Indian Physical Geography
Why in News:
The Odisha government has allocated ₹855 crore for the renovation of the six-decade-old canal system of the Hirakud Dam. This project will benefit farmers in Sambalpur, Subarnapur, Bargarh, and Balangir districts by improving irrigation efficiency and reducing water wastage.
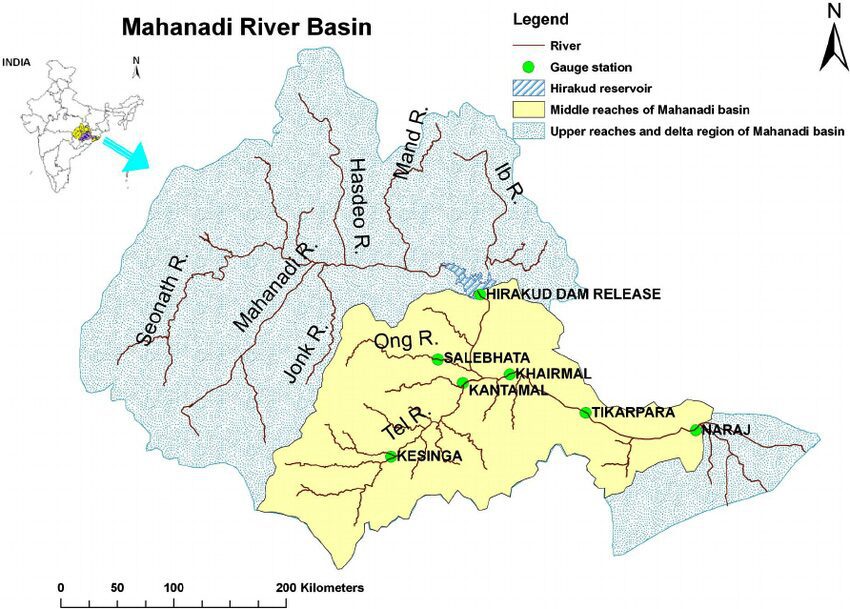
About Hirakud Dam:
Located across the Mahanadi River, Hirakud Dam is the world’s longest earthen dam and was one of India’s first post-independence multipurpose river projects, designed to regulate flooding and provide irrigation.
- It spans 26 km, creating Asia’s largest man-made lake.
- Provides irrigation to 436,000 hectares and generates 359.8 MW of power.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The Hirakud Reservoir created by the dam is the largest artificial lake in Asia, used for irrigation and flood control. |
| Background | The Hirakud Dam was built to manage the seasonal flooding of the Mahanadi River and is key to agriculture in the delta region. |
| Interesting Fact | The dam protects 9,500 sq km of land in Odisha from floods and provides irrigation to over 155,000 hectares of Kharif crops. |
| Relevance | Studying major irrigation and flood control projects like the Hirakud Dam is crucial for topics on water resource management and agricultural geography. |
5. India’s Energy Demand to Triple by 2050
Sub: Economics | Section: Infrastructure
Context:
India’s energy demand is set to triple by 2050, making it a critical player in the global energy transition. With its GDP growing at 7%, India is now the third-largest power market in the world, and energy consumption has risen by over 8% in the past year.
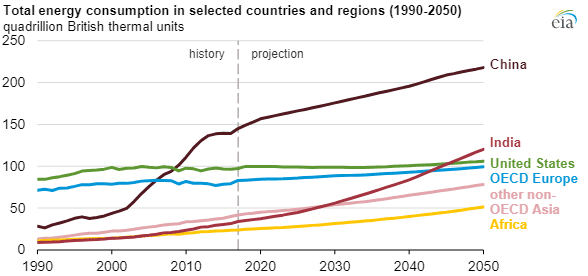
India’s Energy Transition:
- India’s renewable energy sector is rapidly expanding, with over 200 GW of solar and wind capacity expected by 2030.
- Despite the growth of renewables, coal still accounts for 70% of India’s power generation, and 50 GW of coal capacity is expected by 2030.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | India is the second-largest solar module manufacturer globally, with exports to key markets worldwide. |
| Background | India’s growing energy demand is fueled by urbanization, industrialization, and a rapidly expanding middle class. |
| Interesting Fact | India is expected to surpass Germany and Japan in the next 5–10 years to become the world’s third-largest economy. |
| Relevance | Understanding the interplay between economic growth, energy transition, and infrastructure development is essential for topics on sustainable development and energy economics. |
6. Anti-Cancer Drugs to Sport QR Codes to Check Fakes
Sub: Science | Section: Health
Context:
To combat the rise of counterfeit anti-cancer drugs, the Indian government is considering making it mandatory to include quick response (QR) codes on every vial and strip of medication. This would enhance the ability to track and verify genuine pharmaceuticals.
Issue of Counterfeit Drugs:
Counterfeit anti-cancer medications are a growing concern in India, with criminals refilling empty vials of expensive drugs with fake substances. The QR code system will allow better track-and-trace mechanisms for high-risk drugs.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB) is responsible for advising the Indian government on issues related to pharmaceutical safety and approval. |
| Background | Counterfeit drugs have become a global problem, especially for life-saving medications like anti-cancer drugs. India’s pharmaceutical industry faces the challenge of maintaining the integrity of its supply chain. |
| Interesting Fact | The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme has been introduced to boost domestic manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, including anti-cancer drugs. |
| Relevance | This is crucial for topics related to public health and pharmaceutical safety in India, as well as efforts to regulate and improve healthcare infrastructure. |
7. Two Months On, Meghalaya Polio Case Shrouded in Secrecy
Sub: Science | Section: Health
Background:
A recent polio case in Meghalaya has raised concerns due to the government’s lack of transparency. Reports indicate conflicting statements from officials, leading to fears of a cover-up, similar to how the Indian government was criticized for not fully disclosing Zika virus cases in 2017.
Vaccine-Derived Polio (VDP):
The polio case in question appears to be vaccine-derived, caused by a strain of poliovirus that mutated from the strain in the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV). This rare situation can occur when the weakened virus in OPV mutates and circulates in under-vaccinated communities.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV) is rare but can cause outbreaks in areas with poor sanitation and low vaccination coverage. |
| Background | Polio was eradicated from India in 2014, but vaccine-derived cases can still arise in communities where polio vaccination coverage is incomplete. |
| Interesting Fact | India switched to using the Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) after eradicating wild polio, though OPV is still used in some cases. |
| Relevance | This case highlights the need for sustained immunization efforts and the challenges of managing public health risks in developing regions. |
8. World Bank Mulls 27 of 30 Ideas on MDBs by G20 Independent Group
Sub: International Relations | Section: International Organizations
Context:
India’s Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently praised the World Bank for considering 27 of the 30 recommendations made by the G20 Independent Expert Group on Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs). The reforms aim to enhance the role of MDBs in providing financial assistance for global development.
G20 Independent Expert Group (IEG):
This group was appointed during India’s 2023 G20 Presidency. It proposed reforms to triple sustainable lending levels by 2030, including eliminating extreme poverty and increasing support for global public goods like climate action.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) provide financial and technical support for development projects in low- and middle-income countries. |
| Background | The World Bank Group is one of the largest MDBs, alongside the Asian Development Bank and African Development Bank. |
| Interesting Fact | The G20 Expert Group has called for tripling sustainable lending to address challenges like climate change, poverty, and inequality by 2030. |
| Relevance | These reforms are critical for topics on global governance, international financial institutions, and development economics. |
9. What’s Behind Israel’s Ban on the UN Chief?
Sub: International Relations | Section: Places in News
Context:
Israel recently announced that it has banned United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres from entering the country. Israel accused him of supporting groups like Hamas and Hezbollah, while failing to condemn missile attacks by Iran and the Hamas attack on Israel in 2022.
Historical Precedent:
Israel has previously banned UN officials for perceived bias, but banning the UN Secretary-General is unprecedented. A similar event occurred in 1950 when the USSR accused then-UNSG Trygve Lie of bias during the Korean conflict.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Article 100 of the UN Charter states that UN members must respect the international nature of the Secretary-General’s responsibilities. |
| Background | Israel has long argued that the UN is biased in favor of Arab and Islamic nations, citing the role of organizations like UNRWA, which Israel claims is linked to Hamas. |
| Interesting Fact | The UN Secretary-General is appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the UN Security Council. |
| Relevance | This issue is important for understanding international diplomacy, UN functioning, and Middle East geopolitics. |
10. Revitalization of India’s Electric Mobility Sector
Sub: Economics | Section: Infrastructure
Context:
India’s electric vehicle (EV) market is growing rapidly, with major automakers establishing battery assembly plants to meet rising demand. The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme has facilitated the creation of 50 gigawatt hours (GWh) of battery manufacturing capacity.
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
The intermittency of renewable energy sources has made battery energy storage a crucial technology for ensuring grid stability. The Viability Gap Funding (VGF) scheme supports large-scale battery storage systems, targeting an installed capacity of 4,000 megawatt hours (MWh) by 2030.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | India’s lithium-ion battery demand is expected to rise from 10 GWh today to 200 GWh by 2035, driven by the EV sector. |
| Background | India is set to produce 150 GWh of lithium-ion batteries by 2030, meeting 13% of the global demand for battery cells. |
| Interesting Fact | India is the world’s second-largest solar module manufacturer and is rapidly expanding its renewable energy capacity. |
| Relevance | The growth of the EV sector is central to sustainable development, energy infrastructure, and India’s goal of achieving net-zero emissions. |
11. Israel’s Military and Civilian Dual-use Port in Great Nicobar
Sub: Geography | Section: Economic Geography
Context:
As part of the Great Nicobar Development Project, India is planning to build a dual-use International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), which will serve both military and civilian functions. This includes a Greenfield Airport, a power plant, and a township for personnel involved in the project.
Great Nicobar Island:
The southernmost island of India, Great Nicobar, is home to endangered species like the giant leatherback turtle and the Nicobar megapode. The development has sparked environmental concerns, as it requires clearing 130 sq km of forest.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The Great Nicobar Development Project will divert 9.64 lakh trees, raising significant environmental concerns. |
| Background | The Great Nicobar Island is strategically located at the crossroads of key maritime routes, making it an important site for military operations and trade. |
| Interesting Fact | The Nicobar crab-eating macaque and the Nicobar tree shrew are among the endemic species found on Great Nicobar Island. |
| Relevance | This project is important for understanding infrastructure development, biodiversity conservation, and India’s strategic interests in the Indian Ocean. |


