January 25, 2026 5:45 am
Table of contents:
- 1. India’s Per Capita Income to Rise by $2000 in 5 Years
- 2. WHO Approves First Mpox Diagnostic Test for Emergency Use
- 3. National Agriculture Code (NAC)
- 4. Why We Shouldn’t Worry (Too Much) About an Asteroid Hitting Earth
- 5. Elephant Census in India: How Elephants Are Counted
- 6. Prakrit & Pali: Newly Designated Classical Languages
- 7. National Agriculture Code (NAC)
- 8. WHO Approves First Mpox Diagnostic Test for Emergency Use
- 9. Haitian Gang Massacre Leaves at Least 70 Dead: UN Report
- 10. NIC e-Office System Failure Halts Railway File Operations
- 11. UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago: Implications for India
- 12. Wayanad Landslide Relief: Kerala High Court Seeks Centre’s Response
1. India’s Per Capita Income to Rise by $2000 in 5 Years
Sub: Economics | Section: National Income
Finance Minister’s Statement:
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman highlighted that the coming decades will witness a significant improvement in living standards for Indians. This period will mark a crucial phase in India’s development.
Per Capita Income Projection:
India’s per capita income is expected to rise by $2,000 over the next five years. According to IMF projections, India’s current per capita income stands at $2,730, and it took 75 years to reach this level. However, an additional $2,000 will be added within just five years.
Reduction in Inequality:
Inequality in India has declined, as seen in the Gini Coefficient—a measure of income inequality:
- In rural areas, the Gini coefficient improved from 0.283 to 0.266.
- In urban areas, it improved from 0.363 to 0.314.
Impact of Economic Reforms:
The reduction in inequality is likely to continue as economic reforms from the past decade, along with structural reforms, become more apparent in the data. The effects of the Covid shock are also expected to fade.
Fiscal Discipline Commitment:
The government is committed to reducing the fiscal deficit:
- Fiscal deficit is projected to decline from 5.6% of GDP in FY24 to 4.9% in FY25.
- Fiscal discipline will aid in controlling bond yields and reducing borrowing costs throughout the economy.
Capital Expenditure Growth:
Capital expenditure is projected to grow by 17.1%, reaching ₹11.1 lakh crore in FY25, which accounts for 3.4% of GDP. A larger portion of the fiscal deficit will now be allocated toward capital outlays, highlighting the focus on investment-oriented deficit financing.
Lowering of Subsidies:
Declining commodity prices have reduced the need for higher allocations for fertilizer and fuel subsidies, contributing to restrained growth in revenue expenditure, which is expected to rise by 6.2% year-on-year.
India’s Economic Performance:
India has shown remarkable economic performance in the past decade, jumping from the 10th largest economy to the 5th largest in just five years. High growth rates have been maintained, and inflation has stayed within a manageable range.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | India’s expected rise in per capita income marks the steepest increase in living standards post-independence. |
| Background | The Gini Coefficient measures inequality globally on a scale from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (maximum inequality). |
| Interesting Fact | In 2023, India overtook the UK to become the 5th largest economy despite global inflationary challenges. |
| Why It Matters? | This growth in per capita income will elevate India toward middle-income status and improve living standards significantly. |
2. WHO Approves First Mpox Diagnostic Test for Emergency Use
Sub: Science | Section: Health
Why In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has approved the first Mpox diagnostic test under its Emergency Use Listing (EUL). This approval is pivotal in expanding diagnostic capabilities and curbing the spread of Mpox, particularly in regions like Africa, where outbreaks are prevalent.

WHO’s First Emergency Use-Listed Mpox Diagnostic Test:
The Alinity m MPXV assay, developed by Abbott Molecular Inc, has been approved by the WHO as the first in vitro diagnostic test for Mpox under the EUL. This real-time PCR test can detect monkeypox virus DNA (Clade I/II) from human skin lesion swabs, ensuring rapid and accurate diagnosis.
Impact of the Mpox Virus:
In 2024, Africa reported over 30,000 suspected cases of Mpox. Limited testing capacity in the region has hampered efforts to control the virus’s spread, delaying proper diagnosis and containment.
How the Alinity m MPXV Assay Works:
- Detects Mpox virus (Clade I/II) DNA from skin lesion swabs.
- Uses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for precise virus identification.
- Provides fast confirmation in suspected cases.
- Approved by WHO under the EUL to respond to Mpox outbreaks effectively.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Mpox is a zoonotic viral disease that spreads through physical contact with infected individuals, contaminated materials, or animals. |
| Background | Mpox was first identified in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and became a global concern during the 2022 outbreak. |
| Interesting Fact | The Mpox virus has two clades: Clade I, which is deadlier, and Clade IIb, responsible for the global outbreaks in recent years. |
| Why It Matters? | The Alinity m MPXV assay will improve diagnostic capacity, especially in Africa, enabling quicker detection and containment of outbreaks. |
3. National Agriculture Code (NAC)
Sub: Schemes | Section: Agriculture
What is the NAC?
The National Agriculture Code (NAC) is being developed by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). It is similar to the National Building Code and National Electrical Code, aiming to create comprehensive standards for agriculture across India.

National Agriculture Code
Why is the NAC Needed?
While BIS already sets standards for agricultural machinery like tractors and harvesters, many critical areas in agriculture—such as field preparation, micro-irrigation, and water use—lack established standards. The NAC will provide a unified framework to address these areas and guide both policymakers and farmers.
Key Components of the NAC:
The NAC will cover the entire agricultural cycle and will serve as a reference guide for farmers, agricultural universities, and field officials. It will establish general principles for all crops and crop-specific standards for major crops such as paddy, wheat, oilseeds, and pulses.
What the NAC Will Cover:
- Agricultural machinery and processes.
- Post-harvest operations: crop selection, land preparation, irrigation, soil/plant health, harvesting, primary processing, sustainability, and record maintenance.
- Input management: chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and weedicides.
- Crop storage and traceability.
- Emerging areas: natural farming, organic farming, and IoT-based agriculture.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The National Agriculture Code will also focus on modern practices like IoT-based agriculture and SMART farming. |
| Background | Currently, many agricultural practices in India lack comprehensive standards, leading to inefficiencies in field preparation, water management, and resource use. |
| Interesting Fact | The NAC will address the socio-economic diversity of Indian agriculture, providing region-specific solutions tailored to agro-climatic zones. |
| Why It Matters? | The NAC will ensure more efficient, sustainable, and modernized agricultural practices across the country, benefitting farmers and policymakers. |
4. Why We Shouldn’t Worry (Too Much) About an Asteroid Hitting Earth
Sub: Science | Section: Space Sector
Context:
Asteroid 2024 ON, the size of the Eiffel Tower and shaped like a peanut, was initially considered a potential threat but later deemed harmless. It is 370 meters in diameter and traveled at a speed of 40,000 kilometers per hour. Despite concerns, astronomers confirmed that the asteroid would pass by Earth at a safe distance of over a million kilometers, more than twice the distance to the moon.
Near-Earth Objects (NEOs):
NEOs are asteroids or comets that come close to Earth’s orbit. They are defined by a perihelion (closest distance to the sun) of less than 195 million kilometers. The Earth is about 150 million kilometers from the sun, placing NEOs in our solar neighborhood. Scientists have cataloged around 34,000 NEOs, none of which currently pose an imminent threat to Earth.
Asteroid Impact Likelihood:
- Smaller NEOs: Tiny NEOs hit Earth daily, but larger impacts are extremely rare.
- Larger NEOs: Asteroids the size of 2024 ON might strike Earth once every 10,000 years.
- Earth faces daily impacts from approximately 100 tons of space debris, but they consist mostly of tiny rocks that burn up in the atmosphere.
- Larger objects: Those over 1 kilometer in diameter, like the one that caused the extinction of the dinosaurs, may impact Earth once every 260 million years.
NEO Tracking Efforts:
Efforts to track NEOs include the retired NEOWISE telescope, which discovered over 158,000 NEOs. Its successor, the NEO Surveyor, is set to launch in 2027 to continue detecting potentially hazardous asteroids.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The upcoming Vera Rubin Observatory in Chile will create a time-lapse map of the universe, helping track asteroids and improve discovery rates. |
| Background | The DART mission successfully tested NASA’s planetary defense strategy by intentionally crashing a spacecraft into an asteroid to alter its path. |
| Interesting Fact | An asteroid the size of 2024 ON only poses a significant threat to Earth every 10,000 years. Most space debris that hits Earth burns up in the atmosphere. |
| Why It Matters? | While asteroid impacts are rare, continued advancements in tracking technology like NEO Surveyor ensure preparedness for potential future threats. |
5. Elephant Census in India: How Elephants Are Counted
Sub: Environment | Section: Species in News
Context:
The Indian government’s 2022-23 elephant census is facing delays, with the Environment Ministry postponing the release of the Status of Elephants in India report due to incomplete data from the Northeast. Preliminary results show a significant decline in elephant populations, especially in southern West Bengal, Jharkhand, Odisha, and Kerala.
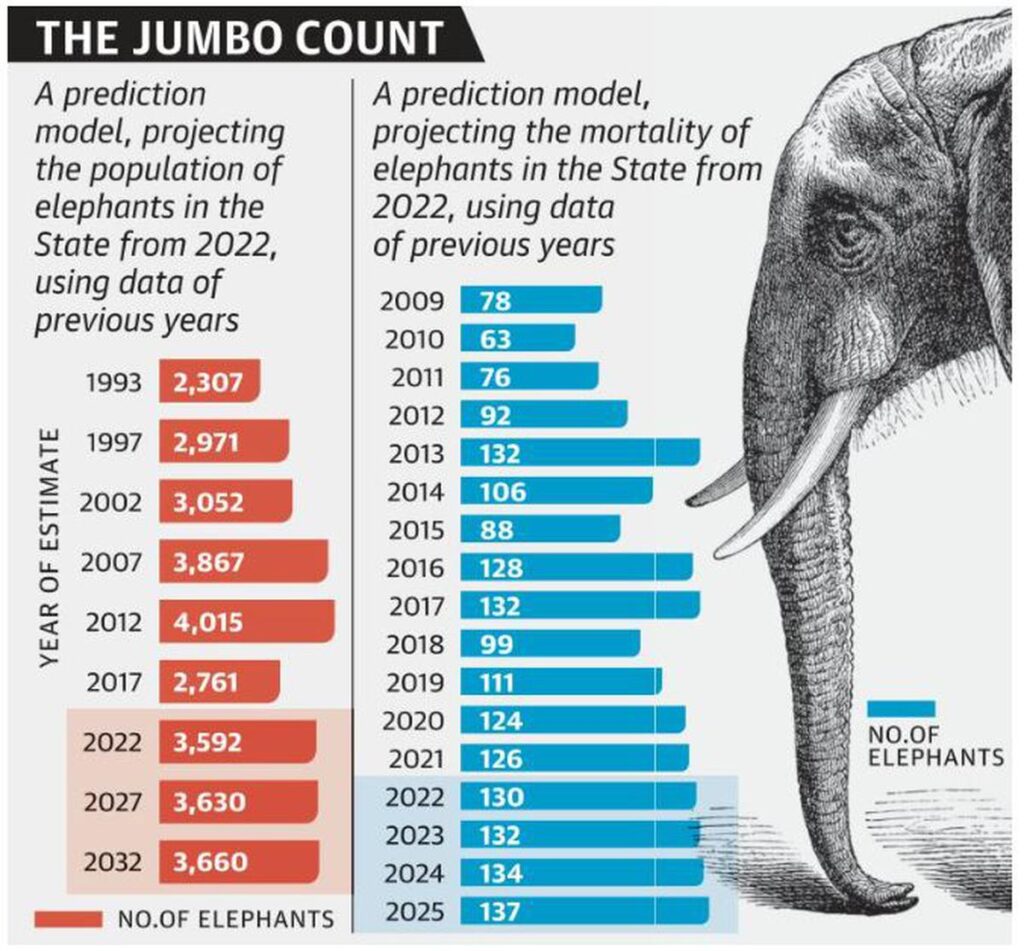
Decline in Elephant Populations:
- Southern West Bengal: Elephant populations have decreased by 84%.
- Jharkhand: 64% decline.
- Odisha: 54% decline.
- Kerala: 51% decline.
Reasons for Decline:
Factors contributing to the decline include unregulated mining, infrastructure projects, and other developmental activities that have disrupted elephant habitats.
Counting Methods:
Elephant census techniques have evolved significantly:
- Old Methods (Pre-2002): The Total Direct Count method was used, which was an unreliable headcount.
- Indirect Dung Count (Post-2002): This method used elephant dung decay rates and defecation rates to estimate populations across pre-selected paths.
- Sample Block Counts: These were used in limited areas to extrapolate population estimates for larger regions.
New Method (2022-23 Census):
The 2022-23 elephant census uses a genetic mark-recapture model, where elephant dung samples are analyzed for genetic markers to identify individual elephants.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The new elephant census methodology uses genetic markers from dung samples to identify individual elephants, making it more accurate. |
| Background | Elephant populations in India face threats from habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and developmental activities like mining. |
| Interesting Fact | The genetic mark-recapture method for elephants mirrors the technique used in the tiger census, but it substitutes tiger stripes with dung DNA analysis. |
| Why It Matters? | Understanding the sharp decline in elephant populations is essential for conservation efforts, as elephants play a key role in maintaining forest ecosystems. |
6. Prakrit & Pali: Newly Designated Classical Languages
Sub: History | Section: Art and Culture
Context:
Prakrit and Pali were recently granted Classical Language status by the Indian government. Both are derivatives of Sanskrit and were extensively used in ancient India, especially in administrative and religious contexts. Alongside Pali and Prakrit, Marathi, Bengali, and Assamese have also received this status.
Prakrit:
The term “Prakrit” derives from “prakriti,” meaning “source” or “origin.” Prakrit languages evolved from Sanskrit and were considered simpler, serving as the language of the masses. Magadhi Prakrit, used by the Mauryan Empire, evolved into modern languages such as Bengali and Assamese.
- Magadhi Prakrit: The language of the Mauryan court, used in the Ashokan edicts.
- Shauraseni Prakrit: Used in North India, evolving into Hindi, Punjabi, and other related languages.
- Ardhamagadhi Prakrit: Prominently used by Jain scholars.
Pali:
Pali is closely related to Magadhi Prakrit and is best known as the language of the Theravada Buddhist canon. The Tripitaka, or the three baskets of Buddhist scriptures, is written in Pali. While Theravada Buddhism declined in India, Pali remains important in Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and other Southeast Asian nations.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Prakrit was the language of the common people in ancient India, while Sanskrit was used by the elites. |
| Background | Pali continues to be the religious language of Theravada Buddhism, and the Tripitaka remains the core text in the tradition. |
| Interesting Fact | The Ashokan edicts, key to understanding the Mauryan Empire, were written in Magadhi Prakrit. |
| Relevance | Understanding Prakrit and Pali is critical for studying ancient Indian history, particularly for Buddhist and Jain texts and inscriptions like the Ashokan edicts. |
7. National Agriculture Code (NAC)
Sub: Schemes | Section: Agriculture
What is the NAC?
The National Agriculture Code (NAC) is being developed by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). It aims to create comprehensive standards for agricultural practices across India, much like the National Building Code and National Electrical Code.
Why is the NAC Needed?
Currently, while the BIS sets standards for agricultural machinery, there are significant gaps in other critical areas such as field preparation, irrigation, and water management. The NAC will fill these gaps by setting standards for all agricultural activities.
Key Components of the NAC:
- Standards for agricultural machinery and processes.
- Post-harvest operations: crop selection, irrigation, soil/plant health, harvesting, sustainability, and record maintenance.
- Input management, including chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and weedicides.
- Crop storage and traceability systems.
- Standards for natural and organic farming, as well as IoT-based agriculture.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The NAC will cover emerging areas of agriculture such as IoT-based farming and SMART farming. |
| Background | The NAC will provide standards for all aspects of farming, from crop selection to post-harvest operations, enhancing sustainability and efficiency in Indian agriculture. |
| Interesting Fact | The NAC will account for agro-climatic zones, crop types, and the socio-economic diversity of Indian agriculture, providing region-specific standards. |
| Relevance | The NAC will guide farmers, policymakers, and agricultural universities in adopting standardized practices that improve productivity and sustainability in Indian agriculture. |
8. WHO Approves First Mpox Diagnostic Test for Emergency Use
Sub: Science | Section: Health
Why In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) recently approved the first Mpox diagnostic test under its Emergency Use Listing (EUL). This test will expand diagnostic capacity and control the spread of Mpox, especially in Africa, which has seen a significant rise in cases.
WHO’s First Emergency Use-Listed Mpox Diagnostic Test:
The Alinity m MPXV assay, developed by Abbott Molecular Inc, is the first Mpox in vitro diagnostic test approved by WHO. This real-time PCR test detects monkeypox virus DNA from human skin lesion swabs, ensuring quick and precise diagnosis.
Impact of Mpox in 2024:
Over 30,000 suspected cases of Mpox were reported in Africa in 2024. Due to limited testing capacity, the virus has spread rapidly, delaying containment efforts.
How the Alinity m MPXV Assay Works:
- Detects monkeypox virus DNA from skin lesion swabs.
- Uses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology for precise virus identification.
- Provides rapid confirmation of Mpox in suspected cases.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Mpox (formerly known as Monkeypox) was declared a global health emergency in 2022 before being downgraded in 2023. |
| Background | Mpox is a zoonotic viral disease that spreads through direct contact with infected individuals, contaminated materials, or animals. |
| Interesting Fact | The Mpox virus has two clades: Clade I (deadlier) and Clade IIb (more transmissible, responsible for recent outbreaks). |
| Relevance | The Mpox diagnostic test expands the global capacity to respond to outbreaks, especially in Africa, where limited diagnostic resources have contributed to the virus’s spread. |
9. Haitian Gang Massacre Leaves at Least 70 Dead: UN Report
Sub: International Relations | Section: Places in News
Context:
The United Nations Human Rights Office reported that a series of gang attacks led by the Gran Grif gang in Haiti resulted in the deaths of at least 70 people. The violence is part of a broader wave of gang-related incidents affecting the Caribbean nation, which has struggled with political instability and lawlessness.
About Haiti:
Haiti, located in the Caribbean, shares the island of Hispaniola with the Dominican Republic. It was colonized by France in the 17th century and became one of the wealthiest colonies due to sugar and coffee plantations. Haiti gained independence in 1804, becoming the first independent Latin American nation.
The Role of UN in Haiti:
The UN has been working with Haitian authorities to restore peace and order, but efforts have been hampered by corruption and the dominance of armed gangs in various parts of the country.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Haiti was the first nation in Latin America to gain independence from European colonization in 1804. |
| Background | Haiti’s political instability and gang violence have worsened since the assassination of President Jovenel Moïse in 2021. |
| Interesting Fact | Haiti was once known as the “Pearl of the Antilles” due to its immense wealth derived from sugar and coffee exports. |
| Relevance | Understanding Haiti’s history and current instability is crucial for International Relations, especially in topics concerning global human rights and UN peacekeeping efforts. |
10. NIC e-Office System Failure Halts Railway File Operations
Sub: Schemes | Section: IT Awareness
Context:
The e-Office system, used by the Indian Railways to manage file movements and departmental communications, experienced a major system failure, halting operations for nearly five days. This incident has raised concerns about the robustness of India’s digital infrastructure and the need for contingency plans for critical systems.
About the e-Office System:
Developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), the e-Office is a cloud-enabled digital platform designed to support effective and transparent intra-government processes. It offers features like two-factor authentication, e-signatures, and digital document management.
Restoration Efforts:
The system was restored by RailTel, a government-owned broadband and VPN service provider responsible for the Railways’ e-Office system. The system is hosted in Tier-III Uptime USA-certified data centers.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The e-Office system is used by 74 ministries and departments in the Government of India for managing unclassified files. |
| Background | The e-Office system, developed by NIC, aims to reduce paperwork, ensure transparency, and increase the efficiency of governmental processes. |
| Interesting Fact | The system downtime affected not only Indian Railways but also other government bodies using the e-Office platform, such as IRCTC and EPFO. |
| Relevance | Issues with government IT infrastructure like the e-Office system are crucial for CSE topics on digital governance, e-Government initiatives, and cybersecurity. |
11. UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago: Implications for India
Sub: International Relations | Section: Places in News
Context:
The United Kingdom has announced plans to cede sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius, ending a long-standing sovereignty dispute over this territory in the Indian Ocean. The Chagos Islands are home to Diego Garcia, a strategic military base operated by the UK and the US, which will remain under UK control for 99 more years.
Historical Background:
The Chagos Archipelago comprises 58 islands and was uninhabited until the late 18th century. It was transferred to British control in 1814 and administratively attached to Mauritius. When Mauritius gained independence in 1968, the UK retained the islands due to their strategic importance, particularly for military operations.
Strategic Importance:
Diego Garcia, the largest island in the archipelago, serves as a critical military base for the US and the UK, supporting operations in the Middle East and monitoring maritime routes like the Malacca Strait.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | Diego Garcia has been used for critical military operations, including in the Gulf War and the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. |
| Background | The sovereignty dispute over the Chagos Islands was brought to the International Court of Justice (ICJ), which ruled in favor of Mauritius in 2019. |
| Interesting Fact | The UN General Assembly voted in favor of Mauritius in 2017, with India supporting the decolonization of the Chagos Archipelago. |
| Relevance | Understanding this treaty is crucial for CSE topics on geopolitics, decolonization, and India’s strategic interests in the Indian Ocean region. |
12. Wayanad Landslide Relief: Kerala High Court Seeks Centre’s Response
Sub: Polity | Section: Miscellaneous
Context:
The Kerala High Court has asked the central government for an explanation regarding the delay in releasing funds from the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) and Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund (PMNRF) for victims of the recent Wayanad landslide. The victims are yet to receive full compensation despite significant damage to life and property.
National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF):
The NDRF is managed by the Central Government under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 and is used to provide relief in the event of natural disasters. It is primarily financed through a National Calamity Contingency Duty (NCCD), levied on certain excisable goods.
Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund (PMNRF):
The PMNRF was established in 1948 to assist displaced persons following the partition of India. Over time, its scope has expanded to support victims of natural and man-made disasters.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| Do You Know? | The NDRF is financed through the levy of excise and customs duties, while the PMNRF is entirely funded by public contributions. |
| Background | The National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) supplements the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) when state-level funds are inadequate for severe calamities. |
| Interesting Fact | The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) is responsible for auditing the accounts of the NDRF. |
| Relevance | This case is crucial for understanding disaster management, fund allocation processes, and the functioning of disaster relief schemes in India. |


